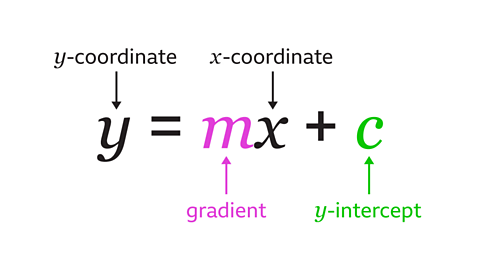Key points
A quadraticDescribing an expression of the form ØÆéØÆÖ┬▓ + ØÆāØÆÖ + ØÆä where ØÆé, ØÆā and ØÆä are real numbers. ØÆÜ = ØÆéØÆÖ┬▓ + ØÆāØÆÖ + ØÆä is a quadratic equation, its graph is a parabola. graph is a visual representation of a quadratic equation in the form \(y = ax┬▓ + bx + c\) where the coefficientA number or symbol multiplied with a variable or an unknown quantity in an algebraic term. Eg, 5 is the coefficient of 5ØÆÅ \(a\) and \(b\) are integerIntegers are numbers with no fraction or decimal part. They can be positive, negative or zero. 42, 8, and 10000 are examples of integers., and \(c\) is a constantThe number or quantity that does not vary. Eg, in the equation ØÆÜ = 3ØÆÖ + 6, the 3 and 6 are constants, where ØÆÖ and ØÆÜ are variables. .
A linear graph can be drawn using only three points. A quadratic graph is a curve, so more points are plotted to support accuracy.
The shape of a quadratic graph is called a parabolaThe shape of a quadratic graph., which looks like a U-shape. When the \(x┬▓\) term is positive the graph is U-shaped. When \(x┬▓\) is negative the graph is šł-shaped. The graph has a vertical line of symmetry.
Understanding how to substitute values into an expression is an essential skill when using graphs to estimate values of \(x\) and \(y\).

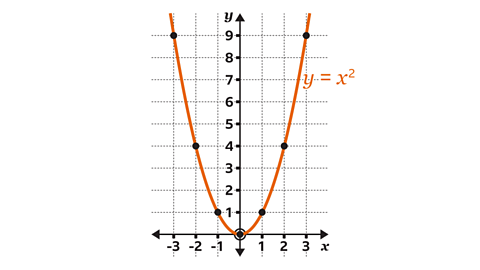
How to draw the graphs ØÆÜ = ØÆÖ┬▓ and ØÆÜ = -ØÆÖ┬▓
There are no straight-line segments on a quadratic graph. The coordinates \((x, y)\) are plotted and joined by drawing a freehand curve.
- Two consecutive horizontal points are joined by a rounded curve.
- A single point is rounded off to avoid a pointed turn.
To draw the graph \(y = x┬▓\):
Set up a table of values for \(x\) and \(y\), using the given values of \(x\)
Find the values for \(y\)
- For \(y = x┬▓\), work out \(x┬▓\) (which is \(x\) multiplied by itself).
- For \(y = -x┬▓\), work out \(-x┬▓\) (which is the negative value of \(x┬▓\)).
Draw and label the axes to include the minimum and maximum values of \(x\) and \(y\).
The coordinates \((x, y)\) are read from the table and plotted on the axes.
Join the points, drawing a freehand curve through the points.
Label the graph.
Examples
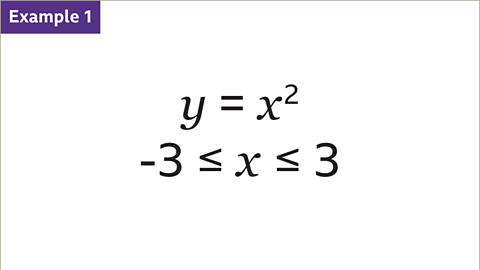
Image caption, Draw the graph of the quadratic equation ØÆÜ = ØÆÖ┬▓ for values of ØÆÖ from -3 to 3. This is shown by the inequality -3 Ōēż ØÆÖ Ōēż 3
Image caption, Set up a table of values using the given values of ØÆÖ from -3 to 3. There are two rows, one for the ØÆÖ values and one for the ØÆÜ values, which are ØÆÖ┬▓
Image caption, Substitute each value of ØÆÖ to find the ØÆÜ values using the equation ØÆÜ = ØÆÖ┬▓. This means that ØÆÖ is multiplied by itself. (-3)┬▓ = 9, (-2)┬▓ = 4, (-1)┬▓ = 1, 0┬▓ = 0, 1┬▓ = 1, 2┬▓ = 4 and 3┬▓ = 9. The values in the table are all positive, because square numbers are always positive, and they mirror each other. Eg, (-3)┬▓ is the same as 3┬▓, and (-2)┬▓ is the same as 2┬▓
Image caption, Draw and label the axes to include the minimum and maximum values of ØÆÖ and ØÆÜ. The ØÆÖ-axis is drawn using the given values from -3 to 3. The ØÆÜ-axis is drawn using values from 0 to 9, which are worked out using ØÆÜ = ØÆÖ┬▓
Image caption, Use the pairs of values in the table to list the coordinates of the points to be plotted. The coordinates are (-3, 9), (-2, 4), (-1, 1), (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 4) and (3, 9). Plot the coordinates on the graph.
Image caption, Join the points, drawing a freehand curve through the points, and label the graph.
Image caption, Draw the graph of the quadratic equation ØÆÜ = -ØÆÖ┬▓ for values of ØÆÖ from -3 to 3. This is shown by the inequality -3 Ōēż ØÆÖ Ōēż 3
Image caption, Set up a table of values using the given values of ØÆÖ from -3 to 3. There are two rows, one for the ØÆÖ values and one for the ØÆÜ values (-ØÆÖ┬▓). Substitute each value of ØÆÖ to find the ØÆÜ values, using the equation ØÆÜ = -ØÆÖ┬▓. As all square numbers (ØÆÖ┬▓) are positive, all the values of -ØÆÖ┬▓ are negative. The values also mirror each other, -9, -4, -1, 0, -1, -4, -9...
Image caption, Use the pairs of values in the table to list the coordinates of the points to be plotted. The coordinates are (-3, -9), (-2, -4), (-1, -1), (0, 0), (1, -1), (2, -4) and (3, -9). Plot the coordinates on the graph and join using a freehand curve. The parabola is šł-shaped when ØÆÜ = -ØÆÖ┬▓
Image caption, There are no straight-line segments on a quadratic graph. Two consecutive horizontal points are joined by a rounded curve. A single point is rounded off to avoid a pointed turn.
1 of 10
Question
Which graph, A, B or C, shows \(y = x┬▓\)?
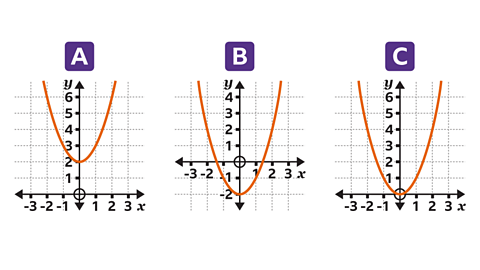
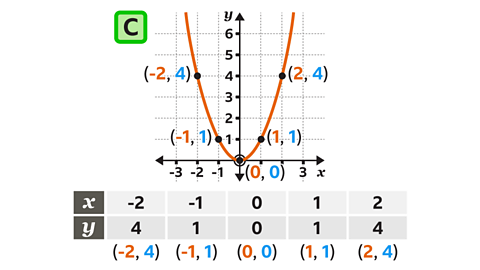
Graph C is \(y = x┬▓\). For each value of \(x\) the value of \(y\) is \(x┬▓\)
- The integer values of \(x\) that can be seen are -2, -1, 0, 1 and 2
- The values of \(y\) (\(x┬▓\)) are 4, 1, 0, 1 and 4
- The integer coordinates (\(x, y\)) are (-2, 4), (-1, 1), (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 4)
Graph A is \(y = x┬▓ +2\)
Graph B is \(y = x┬▓ ŌĆō 2\)
How to draw a quadratic graph from a table of values
A quadratic equation in the form \(ax┬▓ + bx + c\) combines several termAn element within an algebraic sentence. Elements (terms) are separated by + or - signs. .
A table of values is used to find the points to plot for a graph. A row is used for each term in the equation to work out the coordinates.
To draw a quadratic graph from an equation:
- Set up a table of values using the given values of \(x\)
- Use additional rows in the table to work out each term in the quadratic equation.
- Substitute the values of \(x\) to evaluate each term, a row at a time.
- Add up the terms of the quadratic expression, a column at a time, to find the value of \(y\)
- Draw and label the axes to include the minimum and maximum values of \(x\) and \(y\)
- Read the coordinates (\(x, y\)) from the table and plot on the axes.
- Join the points, drawing a freehand curve through the points.
- Label the graph.
Example
Image caption, Draw the graph of the quadratic equation ØÆÜ = ØÆÖ┬▓ + 2ØÆÖ ŌĆō 3 for values of ØÆÖ from -4 to 2. This is shown by the inequality -4 Ōēż ØÆÖ Ōēż 2
Image caption, Set up a table of values using the given values of ØÆÖ from -4 to 2. Each row of the table is a term in the quadratic equation. There is a row for the values of ØÆÖ┬▓, a row for the values of +2ØÆÖ and a row for ŌĆō 3. The final row is for the values of ØÆÜ, which is the sum of the values of ØÆÖ┬▓, +2ØÆÖ and ŌĆō 3
Image caption, Substitute the values of ØÆÖ to evaluate each term, one row at a time. The first row is the term ØÆÖ┬▓. This means that ØÆÖ is multiplied by itself. (-4)┬▓ = 16, (-3)┬▓ = 9, (-2)┬▓ = 4, (-1)┬▓ = 1, 0┬▓ = 0, 1┬▓ = 1 and 2┬▓ = 4
Image caption, The second row is for the term +2ØÆÖ. This is 2 multiplied by ØÆÖ. 2 ├Ś -4 = -8, 2 ├Ś -3 = -6, 2 ├Ś -2 = -4, 2 ├Ś -1 = -2, 2 ├Ś 0 = 0, 2 ├Ś 1 = 2 and 2 ├Ś 2 = 4
Image caption, The third row is the term ŌĆō 3. The term ŌĆō 3 is a constant of 3 being subtracted. ŌĆō 3 is written across the row.
Image caption, Add up the terms of the quadratic expression, a column at a time, to find the value of ØÆÜ. The value of ØÆÜ when ØÆÖ = -4 is found by adding the values of ØÆÖ┬▓ (16), +2ØÆÖ (-8) and ŌĆō 3. The calculation is 16 ŌĆō 8 ŌĆō 3 = 5. Repeat the process for each given ØÆÖ-coordinate. The values of ØÆÜ are 5, 0, -3, -4, -3, 0 and 5. Use the pairs of values in the table to list the (ØÆÖ, ØÆÜ) coordinates of the points to be plotted. The coordinates are (-4, 5), (-3, 0), (-2, -3), (-1, -4), (0, -3), (1, 0) and (2, 5).
Image caption, Draw and label the axes to include the minimum and maximum values of ØÆÖ and ØÆÜ. The ØÆÖ-axis is drawn using the given values from -4 to 2. The ØÆÜ-axis is drawn using values from -4 to 5, worked out using ØÆÖ┬▓ +2ØÆÖ ŌĆō 3
Image caption, Plot the coordinates (-4, 5), (-3, 0), (-2, -3), (-1, -4), (0, -3), (1, 0) and (2, 5).
Image caption, Join the points, drawing a freehand curve through the points. Label the graph.
1 of 9
Questions
Question 1:
Complete the table for \(y = x┬▓ ŌĆō 4x + 5\) for values of \(x\) from ŌĆō1 to 3
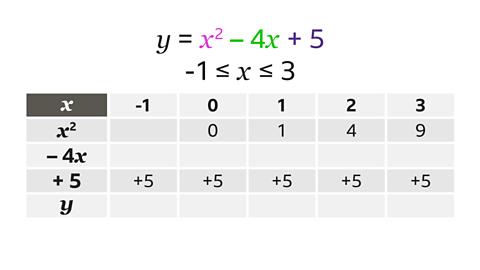
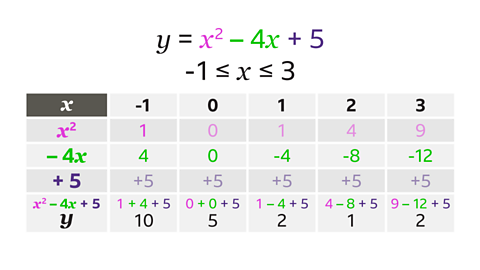
In the \(x┬▓\) row, (-1)┬▓ is the missing value. This is -1 ├Ś -1 = 1
The entire -4\(x\) row must be completed. This is -4 multiplied by each \(x\) value.
- When \(x\) = -1, -4\(x\) = -4 ├Ś ŌĆō1, -4\(x\) = 4
- When \(x\) = 0, -4\(x\) = -4 ├Ś 0, -4\(x\) = 0
- When \(x\) = 1, -4\(x\) = -4 ├Ś 1, -4\(x\) = -4
- When \(x\) = 2, -4\(x\) = -4 ├Ś 2, -4\(x\) = -8
- When \(x\) = 3, -4\(x\) = -4 ├Ś 3, -4\(x\) = -12
The \(y\)-coordinates are found by adding together the terms \(x┬▓\), -4\(x\) and + 5
- When \(x\) = -1, \(y\) = 1 + 4 + 5, \(y\) = 10
- When \(x\) = 0, \(y\) = 0 + 0 + 5, \(y\) = 5
- When \(x\) = 1, \(y\) = 1 ŌĆō 4 + 5, \(y\) = 2
- When \(x\) = 2, \(y\) = 4 ŌĆō 8 + 5, \(y\) = 1
- When \(x\) = 3, \(y\) = 9 ŌĆō 12 + 5, \(y\) = 2
Question 2:
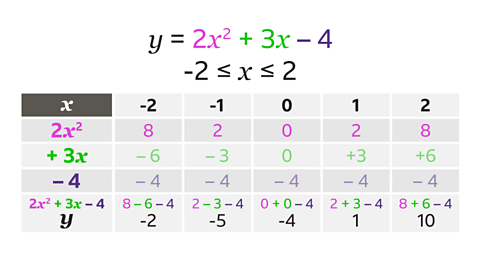
Complete the table for \(y = 2x┬▓ + 3x ŌĆō 4\) for values of \(x\) from ŌĆō2 to 2
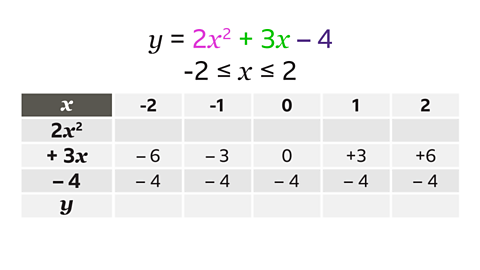
The entire \(2x┬▓\) row must be completed. This is 2 multiplied by each \(x┬▓\) value.
- When \(x =\) -2, \(2x┬▓ =\) 2 ├Ś (-2)┬▓, \(2x┬▓ = 8\)
- When \(x =\) -1, \(2x┬▓ =\) 2 ├Ś (-1)┬▓, \(2x┬▓ = 2\)
- When \(x =\) 0, \(2x┬▓ =\) 2 ├Ś 0┬▓, \(2x┬▓ = 0\)
- When \(x =\) 1, \(2x┬▓ =\) 2 ├Ś 1┬▓, \(2x┬▓ = 2\)
- When \(x =\) 2, \(2x┬▓ =\) 2 ├Ś 2┬▓, \(2x┬▓ = 8\)
The \(y\)-coordinates are found by adding together the terms \(2x┬▓\), \(+3x\) and -4
- When \(x =\) -2, \(y = 8 ŌĆō 6 ŌĆō 4\), \(y =\) -2
- When \(x =\) -1, \(y = 2 ŌĆō 3 ŌĆō 4\), \(y =\) -5
- When \(x =\) 0, \(y = 0 + 0 ŌĆō 4\), \(y =\) -4
- When \(x =\) 1, \(y = 2 + 3 ŌĆō 4\), \(y =\) 1
- When \(x =\) 2, \(y = 8 + 6 ŌĆō 4\), \(y =\) 10
Use a quadratic graph to estimate values of ØÆÖ and ØÆÜ
A quadratic graph can be used to find an estimate of the value of \(x\) from a given value of \(y\), or the value of \(y\) from a given value of \(x\)
A value of \(x\) will give one \(y\)-value.
A value of \(y\) will give two possible values of \(x\) because a quadratic graph is symmetrical.
To find a \(y\)-value from a given \(x\)-value:
- On the \(x\)-axis, locate the given amount.
- Draw a vertical line, using a ruler, from the given amount to the curve.
- Draw a horizontal line, using a ruler, from the curve across to the \(y\)-axis.
- Read the value on the \(y\)-axis.
To find an \(x\)-value from a given \(y\)-value:
- On the \(y\)-axis, locate the given amount.
- Draw a horizontal line, using a ruler, from the given amount across to the curve. It will cross the curve in two places.
- Draw a vertical line, using a ruler, from the curve down to the \(x\)-axis.
- Read the values on the \(x\)-axis.
Examples
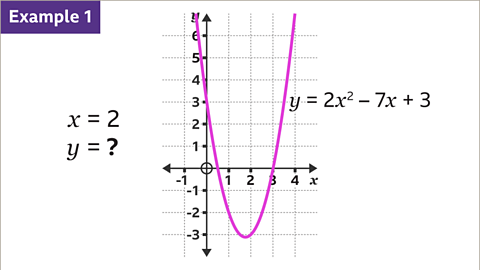
Image caption, Use the graph of ØÆÜ = 2ØÆÖ┬▓ ŌĆō 7ØÆÖ + 3 to find the value of ØÆÜ when ØÆÖ = 2
Image caption, On the ØÆÖ-axis, locate the given value of ØÆÖ (2). Draw a vertical line, using a ruler, down from 2 on the ØÆÖ-axis to the curve.
Image caption, Draw a horizontal line, using a ruler, from the curve across to the ØÆÜ-axis. Read the value on the ØÆÜ-axis. When ØÆÖ is 2, ØÆÜ is -3
Image caption, Use the graph of ØÆÜ = ØÆÖ┬▓ ŌĆō 3ØÆÖ ŌĆō 2 to find the values of ØÆÖ when ØÆÜ = 2
Image caption, On the ØÆÜ-axis, locate the given amount (2). Draw a horizontal line, using a ruler, from 2 on the ØÆÜ-axis across to the curve. It will cross the curve in two places.
Image caption, Draw vertical lines, using a ruler, from the curve down to the ØÆÖ-axis. Read the values on the ØÆÖ-axis. When ØÆÜ = 2, ØÆÖ = -1 and ØÆÖ = 4
1 of 6
Question
Use the graph of \(y = 3 + 4x ŌĆō x┬▓\) to find the values of \(x\) when \(y = 3\)
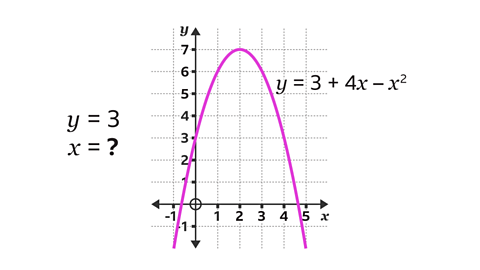
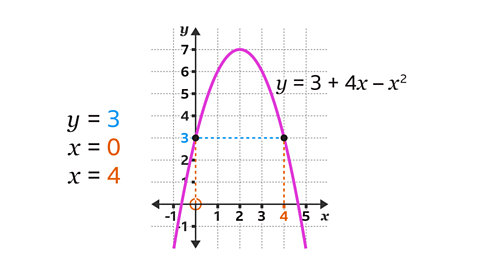
On the \(y\)-axis, locate the given value of \(y\) (3).
Draw a horizontal line, using a ruler, from 3 on the \(y\)-axis across to the curve. It will cross the curve in two places.
Draw vertical lines, using a ruler, from the curve down to the \(x\)-axis.
Read the values on the \(x\)-axis. When \(y\) = 3, \(x\) = 0 and \(x\) = 4
Practise reading and plotting quadratic graphs
Quiz
Practise reading and plotting quadratic graphs with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Real-life maths
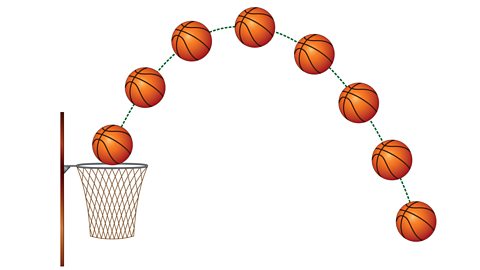
A parabola is the shape of a quadratic graph.
Understanding this shape can be helpful to many types of sports athletes. An object thrown or kicked through the air will create a parabola.
A netball or basketball player could create digital quadratic graphs to analyse their shooting technique, for example. A rugby or football player could do the same when practising conversions or free kicks.
Doing this can help sports players adjust their throws or kicks and improve their accuracy.

Game - Divided Islands
Play the Divided Islands game! gamePlay the Divided Islands game!
Using your maths skills, help to build bridges and bring light back to the islands in this free game from ▒½ėŃtv Bitesize.

More on Graphs
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 7
- count2 of 7
- count3 of 7
- count4 of 7