What are forests?
Forests are areas mostly covered in trees. They have a huge impact on the environment and our wellbeing so it is important we look after them.
In this article you can learn:
- What a forest is
- Different types of forest
- Why forests are important
- How we can protect and conserve forests
This resource is suitable for Landscapes topics for primary school learners.
Video - Forests
Join Isla and Connor as they explore forests in the Loch Lomond and the Trossachs National Park.
Watch this short video to find out about forests.
ISLA: Have you heard of forest bathing, Connor?
CONNOR: Bathing in a forest? Sounds a bit chilly…
ISLA: It means soaking up the calm atmosphere, breathing the fresh air. Being in nature, like forests, is good for us.
Look at this map of the forest.
Once, Scotland was covered in the ancient Caledonian Forest. Now, only small pockets of the original forest remain in 35 sites. There are newer forests too, like here in the Trossachs.
It’s important we protect and conserve what’s here.
CONNOR: That’s why we need national parks like this one at Loch Lomond and the Trossachs.
ISLA: Yep. Trees trap and store carbon, which helps reduce the impact of climate change, and they soak up water which helps prevent flooding.
In Scotland we have unique areas of forest that support rare and endangered species, like the wildcat, or eagles - and look – that red squirrel!
CONNOR: Aww!
I love the way the sunlight falls through the leaves!
ISLA: Me too. This is a broadleaf or deciduous forest. That means that the trees have wide, flat leaves that catch a lot of sunlight, which the trees need to grow.
They lose the leaves in winter, which helps them save energy and water. You find trees like oak, cherry, birch, beech and elm here.
Because the leaves fall off and rot, the nutrients they contain go back into the soil. Worms in the soil help to blend all the nutrients together to create a rich, fertile, brown soil.
The roots of the trees are deep too, which breaks up rock underground, creating depth to the soil. That means that the soil layer here is thick and a big number of trees and plants can grow and thrive in it.
CONNOR: Those trees and plants are a great food source for plant-eating animals and those animals become food for meat-eaters, carnivores. It's all part of the food web.
ISLA: And these woods aren't just good for animals, forests are also great just for the fun of walking, hiking and exploring the great outdoors. Do you ever feel better than after a good walk in the woods?
CONNOR: It’s great. But I do like a pine forest.
This way!
It feels different here doesn’t it? These are Scots Pines.
ISLA: Yeah. Different trees grow in different climates. Cold northern areas grow pine and fir, while warmer climates grow broadleaf trees.
CONNOR: They’re called coniferous trees because they grow cones - the trees are usually cone-shaped too and their leaves are like thin, needles, which don't lose a lot of heat or water, even in the cold weather.
They keep their leaves all year. This means they can photosynthesise (capture the sun’s energy through their leaves) all year round, making the most of the weaker sunshine in winter. They grow closer together, which also helps keep the forest floor warmer.
ISLA: But because they don’t drop their needles as much, and because when they do the cold weather slows the rotting down, the soil is very thin. As a result, the tree roots can’t get as deep underground.
Natural coniferous forests are still great for wildlife though.
CONNOR: Breathe in that pine-fresh air!
ISLA: It’s like Christmas!
What are the different types of forests?
A forest is an ecosystemA natural environment where living and non-living parts interact. For example, plants, soil and the sun. made up mostly of trees.
The two main types of forest are:
- Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. or broadleaf forests
- Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. forests
Deciduous or broadleaf forests are made up of trees with wide flat leaves. These catch lots of sunlight in summer so the trees can grow. Broadleaf trees lose their leaves in autumn, which helps them save heat and water over winter. Every year the falling leaves add new nutrients to the soil.
Coniferous forests are made up of trees with thin needles. These don't catch as much sunlight as broad leaves. Conifers keep their needles all year round as they do not lose much heat or water through them. Soil in coniferous forest is thin with fewer nutrients as there is no annual leaf material to add to the soil.

Image caption, Broadleaf (deciduous) forests
Broadleaf trees, like oak and birch, have wide flat leaves that catch a lot of sunlight. They lose their leaves in autumn which helps them save energy and water during winter. Their fallen leaves go into the soil so broadleaf forests often have thick fertile soil. (Stephen Peter Street / Alamy Stock Photo)
Image caption, Coniferous forests
Coniferous trees, like pine and fir, grow cones and are often cone-shaped. Their leaves are like thin needles which don't lose a lot of heat or water even in cold weather. (Findlay / Alamy Stock Photo)
1 of 2
Why are forests important?
- Forests are full of trees and other plants, which absorbTo take something in, gradually. For example plants absorb carbon dioxide. carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
- All animals, including humans, breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. This means trees provide us with the oxygen we need to survive.
- By absorbing carbon dioxide, trees prevent pollution, improve air quality and slow down the effects of climate changeThe change in the usual conditions of weather (temperature, wind, rainfall etc.) on Earth over a long period of time. The climate has changed throughout the history of Earth, but current climate-change refers to an increase in global temperature..
- Forests also provide food and shelter for living creatures.
- Forests can help prevent flooding because the roots of trees absorb water.
- Being in nature, like forests, is good for our health and wellbeing. It can help us feel relaxed and calm.
Deforestation
- Deforestation means the removal of trees. This is sometimes done to clear land for farming, roads or settlements. It is a big problem globally.
- For example, in the Amazon Rainforest in South America around 11,000km² of trees were cut down in 2020.
- Trees are removed to make space for things like farmland to raise cattle for the meat industry. That’s the same as around 2 million football pitches worth of trees being cut down in a year. This is not sustainableUsing something in a way that does not destroy it completely..
- In Scotland lots of our forests are now more sustainable. That means that when we cut down trees, we plant new ones to replace them so our forests stay alive and we protect our wildlife and environment.
The Caledonian Forest
Scotland was once covered in the ancient Caledonian Forest. Most of the trees were Scots pine but there were also juniper, oak, holly, birch and rowan.
From the end of the stone age around 4, 000 years ago, parts of the Caledonian Forest were lost as people began to cut down trees for fuel and building with. In the 18th and 19th Century, more forest was cleared to make way for sheep farming. Now, only small pockets of the original forest remain in 35 sites.
The maps below show where the ancient Caledonian Forest could be found 5000 years ago and where it still stands today.
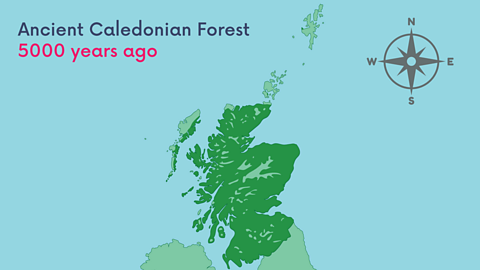
Image caption, The ancient Caledonian Forest 5000 years ago
Image caption, What is left of the ancient Caledonian Forest today
1 of 2

Key words about forests
- forest - A large area, or ecosystem, covered mainly by trees and vegetation.
- ecosystem - A geographic area made up of all of the living and non-living things. It is an area where plants, animals, and other living things, as well as the landscape and weather work together. Ecosystems can be very large or very small.
- forest bathing - A method of relaxation that involves spending time in forests. It is an old technique that was first developed in Japan.
- Caledonian Forest - The ancient forest that once covered the whole of Scotland. It is mostly made up of Scots pine trees.
- conservation - Protecting something from being destroyed or wasted.
- deforestation - The removal of trees. This is sometimes done to clear land for farming, roads or settlement.
- carbon dioxide - A natural gas that is all around us. It is essential for life on Earth. Trees absorb carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. Planting more trees means more carbon dioxide can be absorbed. This helps reduce the effects of global heating and climate change.
- climate change - The long-term change in weather patterns (temperature, wind, rainfall etc.) on Earth, including its side-effects, for example increased drought and flooding.
- endangered species - A group of plants or animals that are at risk of becoming extinct A species that no longer exists. in the near future.
- broadleaf forest - A forest made up of trees with broad leaves, such as oak, beech and elm. They can be found in places with high rainfall, warm summers and cooler winters and lose their leaves in winter. They are also known as deciduous forests.
- coniferous forest - A forest made up of evergreen trees with needles instead of leaves, such as spruce, pine and fir.
- soil - Material that is made up of five things: minerals, organic matter (like animal poo), living organisms (like worms), gas, and water.
- herbivore - An animal that only eats plants.
- carnivore - An animal that only eat meat from other animals.
- food web - A diagram that shows how plants and animals get their energy. This is sometimes called a food chain too. Most food webs start with a green plant, because plants can make their food by photosynthesis.
- photosynthesis - A process in green plants use sunlight to make nutrients from carbon dioxide and water.
Exploring Loch Lomond and the Trossachs
Loch Lomond and the Trossachs is one of two national parkAn area set aside by government to preserve the natural environment. A national park is also set aside because of historical or scientific interest as well as enjoyment by the public. in Scotland. The park is made up of unique forests, rivers, lochs, mountains and wildlife.
Look at this map to see where Loch Lomond and the Trossachs National Park is and some of its main places and features.
How can we protect forests?
In Scotland, we have unique areas of forest that support rare and endangered species Plants and animals that have such low numbers that they are at risk of becoming extinct..
Learn more about how we can conserve Scotland's forests and the wildlife that lives there.
Wood and sustainability. revision-guideWood and sustainability
Find out why wood is used, why trees are important, what deforestation is and how we can make more sustainable choices.

Scottish wildcats. audioScottish wildcats
The Scottish Wildcat lives in the Highlands and is one of the rarest animals in the world. Join the wildlife experts who are working to protect it.

Secrets of a forestry craftsperson. audioSecrets of a forestry craftsperson
Jay Hannah loves working outdoors and looking after the forest so everyone can enjoy it.

Food webs and photosynthesis
In the video at the top of the page we learned about food webs. This is made up of different connected food chains.
- Trees and other plants in forests get nutrientsThe building blocks needed to keep a plant or animal alive and healthy. Animals get most of their nutrients from food. Plants get nutrients from soil and sunlight. and energy from sunlight and the soil to grow.
- These plants become food for plant-eating animals (herbivores). For example, bigger animals, like deer and beavers, and smaller rodents, like squirrels and birds.
- The small animals often become food for meat-eating animals (carnivores). For example, foxes and pine marten.
Find out more about how plants and animals get energy.
What is a food chain? revision-guideWhat is a food chain?
Find out how food chains can show the relationship between different animals and plants.
Food chain challenge - Woodland. interactiveFood chain challenge - Woodland
Can you find different food chains in a woodland habitat?

How do plants get energy and food to grow?
Learn about photosynthesis and respiration, and how plants gain nutrients to grow.

Test your knowledge
Quiz
Challenge

Write a story or poem about a forest.
In this article, we have learned so much about forests. Can you write a story or poem about trees or wildlife that you might find in a forest?
Here are some ideas to inspire you.
More on Landscapes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count23 of 25

- count24 of 25

- count25 of 25

- count1 of 25



