This module builds on: Module 7 (M7) Similar shapes
Similar Shapes
When a shape is enlarged, the image is similar to the original shape. It is the same shape but a different size. Similarity is used with 3-D shapes to solve problems.
Enlargement Effect on Perimeter, Area and Volume
When we enlarge a shape by a scale factor, the length of each edge and the perimeter are multiplied by the scale factor.
When we enlarge a shape by a scale factor, the area of the shape is multiplied by the square of the scale factor.
When we enlarge a shape by a scale factor, the volume of the shape is multiplied by the cube of the scale factor.
Example
Two similar tanks are filled with water. One has a capacity of \(30\text{m}^{3}\), the other a capacity of \(240\text{cm}^{3}\). Calculate the scale factor for the lengths of the tanks and the scale factor for the surface areas.
Solution
Scale factor for volume = \(240 \div 30 = 8\)
Scale factor for length = \(\sqrt[3]{8} = 2\)
Scale factor for area = \(2^2 = 4 \)
Question
The two tins of soup are similar. The volume of the small tin is approximately \(125\text{cm}^{3}\) and the volume of the larger tin is \(500\text{cm}^{3}\).
Calculate the diameter of the larger tin.
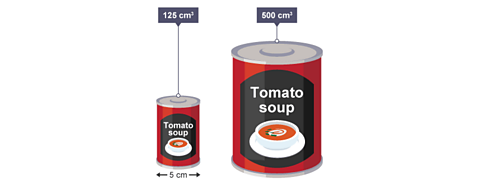
Answer:
The scale factor of the volumes is \(500 \div 125 = 4\)
The scale factor of the lengths will be \(\sqrt[3]{4}\)
The diameter of the larger tin is \(5 \times \sqrt[3]{4} = 7.9\) (1 d.p.)
Ratios
Ratios can also be used to express scale factor.
Example
Two similar pyramids have volumes \(64 \text{cm}^{3}\) and \(343 \text{cm}^{3}\).
What is the ratio of their surface areas?
Solution
Volume ratio = \(64 : 343\)
Length ratio = \(\sqrt[3]{64} ‚à∂ \sqrt[3]{343} = 4 : 7\)
Area ratio = \(4^2 : 7^2 = 16 : 49\)
Question
The diagram shows a large cone of radius 6 cm and height 18 cm and a small cone with height h.
The volume of the large cone is 8 times the volume of the small cone.
Calculate the height, \(h\), of the small cone.
Answer:
Volume ratio = \(8 : 1\)
Length ratio = \( \sqrt[3]{8} ‚à∂ \sqrt[3]{1} = 2‚à∂1\)
\(h = 18 \div 2 = 9 \text{cm}\)
Test yourself
More on M8: Geometry and measures
Find out more by working through a topic