Metals and plastics
The following tools are used for measuring and marking-out when working with metals and plastics:-
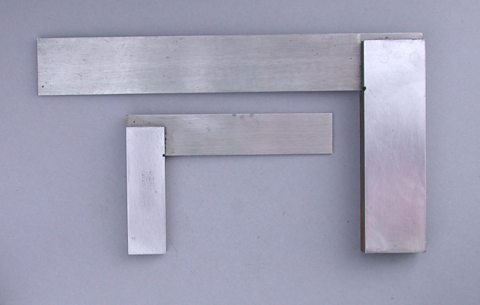
Engineer's square – Used to help draw a perpendicular line on material with a scribe. Must be placed with the flat edge of the handle flat against the workpiece.


Spring dividers – Used to help scribe an arc or a circle on material. They have two legs and look similar to a compass. One of the legs is firmly placed on the material while the other leg is rotated, scribing a circle or arc onto the workpiece.

Scribe – Used to mark a line on a material. It has a sharp point and acts like a pencil to engrave a fine line onto surfaces such metal or plastic where pencils might not work well.
Steel rule - Used to measure materials for cutting or joining. Best used flat against the side and bottom edges. This ensures that measurements are marked from one consistent spot.

Centre punch – Used to mark a centre mark for drilling. Use a hammer to drive the point of the centre punch into the metal. This leaves a small surface impression.

Odd-leg callipers – Used to scribe a parallel mark on metal or plastic. The callipers have two legs – one with a guiding edge with a foot and the other with a scribe point. The guiding edge runs along the edge of the object to be scored while the scribing edge marks a line parallel to the edge.

Inside callipers look similar to odd leg callipers. The are used to measure distances on the inside of materials such as tubes.
These callipers have two legs with guiding feet pointing outwards. The legs are placed inside the material or object to be measured and then extended until the feet make contact with the material. The span of the legs is then measured against a steel rule to give an accurate reading.

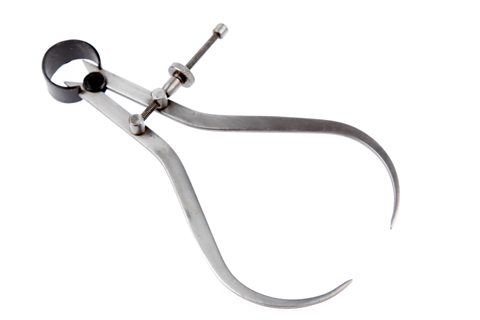
Outside callipers – Used to measure thicknesses and outside diameters or materials. They should be placed round a material and the legs tightened so the guiding feet meet the work piece but can be removed without being adjusted. The span of the legs is then measured against a steel rule to give an accurate reading.
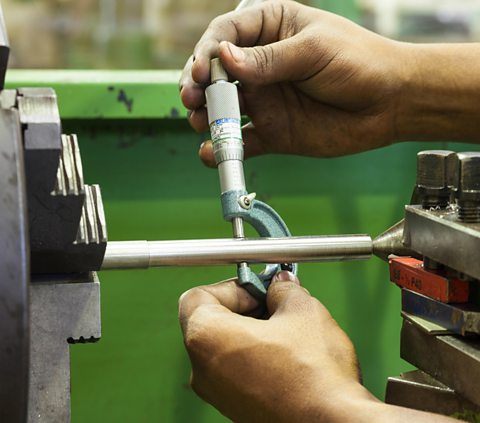


A micrometer – Used to give an extremely precise measurement. Can be used like a more accurate version of an outside callipers and gives an accurate measurement of outside edges of material.
Micrometers are useful when you need a precise measurement rather than using human eye on a steel rule as they have their own gauge.

Marking-out plastics

Chinagraph pencil or marker pen – Used to draw on plastic as it is more visible than pencil and doesn't leave a permanent engraved line like a scribe.
