Features of climate change
The enhanced greenhouse effect
When fossil fuelNatural, finite fuel formed from the remains of living organisms, eg oil, coal and natural gas. are burned, for example by industry, in power stations or in vehicles and aeroplanes, gases are released which enter the atmosphere. Although these gases have always been present in the Earth's atmosphere, their concentration is gradually increasing as more and more fossil fuels are burned.
The build-up of these so-called greenhouse gases The gases responsible for global warming and climate change - carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons). acts like a blanket around the planet, trapping heat inside the Earth's atmosphere.
This is the enhanced greenhouse effectThe retention of heat in the atmosphere caused by the build-up of greenhouse gases. and the resulting increase in global temperatures is called global warmingThe rise in the average temperature of the Earth's surface. or global heating.
Impact of the enhanced greenhouse effect
The build-up of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways:
- The gases allow more of the Sun's rays to enter the atmosphere. Some solar radiationEnergy from the sun - consisting of visible light, heat or infra-red radiation, ultra-violet and other forms of radiation. is still reflected back into space by the outer parts of the atmosphere, but the amount reflected back is gradually reducing.
- At the same time, the greenhouse gases absorb more of the solar radiation that is reflected back from the Earth's surface trapping heat and keeping it in the atmosphere.
The ability of the atmosphere to capture the Sun's energy is essential for life on Earth, but significantly more heat is being captured and this is having a negative impact on the planet.
Variations in global temperature
The diagram below shows variations in global temperature from1850-2020.
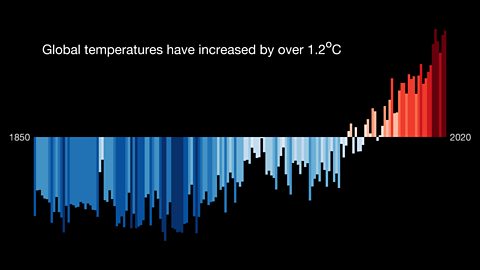
This graph shows that there are variations in the Earthâs average annual temperatures. It also shows that the overall trend, since the 1970s is an increase in global surface temperature. In other words, our Earth is getting hotter.