Transformations
It may be useful to look at M5 Transformations and M6 Transformations
Transformations change the size or position of shapes.
Scale factors can change the size of shapes.
The 4 transformations of 2D shapes:
- Translation - moving a shape in a straight line
- Reflection - flipping a shape to create a mirror image
- Rotation - turning a shape
- Enlargement - changing the size of a shape by a scale factor
It is important to know how to draw and/or describe transformations
M7 transformations looks at
- Reflection - in a diagonal line
- Enlargement - using a fractional scale factor
Reflection in a diagonal line
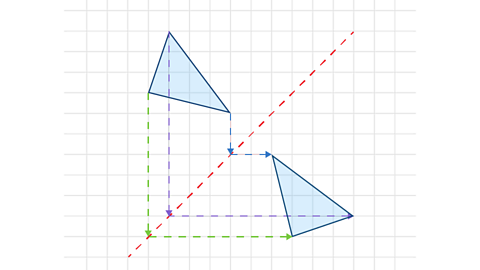
- Draw the line of reflection.
- From a point on the shape, count how far it is vertically from the line of reflection.
- Count the same amount horizontally on the other side of the line and plot the point.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each point in the shape.
It is important to know the names of the diagonal lines.
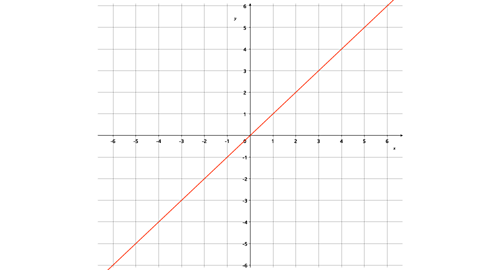
Question
Reflect the shape in the line y = x
The equation of a straight line graph has the form \(\mathbf{y = mx + c}\) where \(\mathbf{m}\) is the gradient and \(\mathbf{c}\) is where the line crosses the \(y\)-axis.
The line \(\mathbf{y = x}\) has a gradient of 1 and crosses the \(\mathbf{y}\)-axis at (0,0).
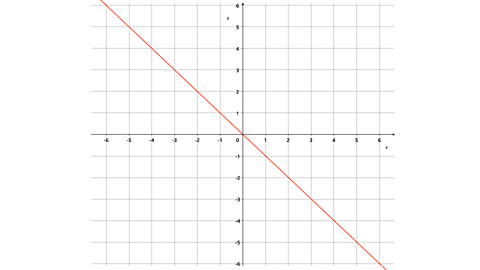
Question
Describe the transformation of the shape ABC.
The mirror line has a gradient of -1 and crosses the \(\mathbf{y}\)-axis at (0,0).
The shape has been reflected in the line \(\mathbf{y = -x}\).

There will be a mark for writing reflection and a mark for writing in the line \(y = - x\)
Enlargement with a fractional scale factor
When a shape is enlarged by a scale factor The ratio of corresponding lengths in similar shapes, ie how much larger or smaller the shapes are. between 0 and 1, the image is smaller than the original shape.
The triangle ABC is enlarged by a scale factor of â…“. All the sides of triangle A'B'C' are one third as long as the sides of the original triangle ABC.
Example
Enlarge the triangle ABC by a scale factor of ½ about the centre of enlargement O.
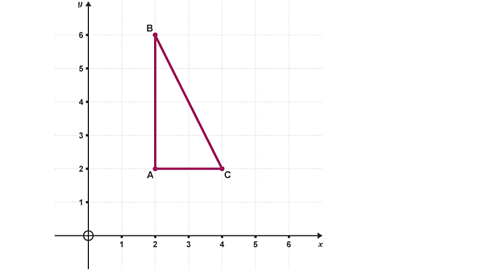
Image caption, First, draw ray lines from O to each corner of the triangle.
Image caption, Next, measure the distance from O to each corner of ABC. Divide the distance by two and plot the points A' B' and C'.
Image caption, Finally, join up the points A' B' C'.
1 of 3
Alternatively these distances can be shown as vectors. \(\text{OA} = \left( \matrix{ 2 \cr 2 \cr} \right)\) so under a scale factor of ½ , \(\text{OA'} = \left( \matrix{ 1 \cr 1 \cr} \right)\).
Finding the centre of enlargement
To find the centre of enlargement, draw ray lines from the corners of the image through the corners of the original shape.
Example
Describe the transformation of the triangle RST.
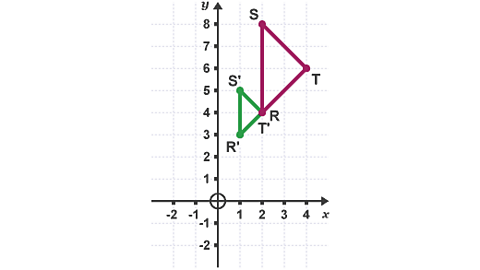
Image caption, Draw ray lines from the corners of triangle RST through the corners of R'S'T' until they cross. This is the centre of enlargement
Image caption, The triangle has been enlarged by a scale factor of ½ about the centre of enlargement (0,2)
1 of 2
Test yourself
More on M7: Geometry and measures
Find out more by working through a topic