Transformations
It may be useful to look at the following topics
Transformations change the size or position of shapes.
Scale factors can change the size of shapes.
Congruent shapes are identical in shape and size but may be reflected or rotated.
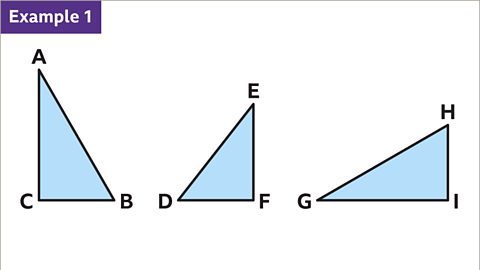
Image caption, Two of these triangles are congruent, which means they are identical in shape and size.
Image caption, Triangles ABC and GHI are congruent. Triangle GHI is the same as ABC but has been rotated 90° anticlockwise. Triangle DEF is a different size.
Image caption, Line segments AB and GH are the same length. BC and HI are the same length. AC and GI are the same length.
Image caption, Angle A and angle G are equal. Angle B and angle H are equal. Angle C and I are equal and are both right angles.
Image caption, These two rectangles are not congruent.
Image caption, Rotating rectangle EFGH and placing it on top of rectangle ABCD shows they are not the same size.
Image caption, These two quadrilaterals are congruent.
Image caption, EFGH is a reflection of ABCD on a vertical mirror line. Line segments AB and EH are the same length. They correspond to each other, which means they are in the same place in two different shapes. BC and GH are the same length. CD and FG are the same length. AD and EF are the same length.
Image caption, Angles in congruent shapes are equal. Angle A and angle E are equal. They correspond to each other. Angle B and angle H are equal. Angle C and G are equal. Angle D and F are equal.
1 of 9
Question
Which shapes are congruent?
Answer
Shapes A, B, E and G are congruent.
There are 4 transformations of 2D shapes that you should know:
- Translation - moving a shape in a straight line
- Reflection - flipping a shape to create a mirror image
- Rotation - turning a shape
- Enlargement - changing the size of a shape by a scale factor
In the exam you may be asked to draw and/or describe transformations.
Translation
When a shape is translated, it is moved up or down and/or left or right. Every point in the shape must be moved in exactly the same way.
Describing translations
Column vectorA vector describes a movement from one point to another. A vector quantity has magnitude (size) and direction.are used to describe translations.
\(\left( \matrix{ 4 \cr -3 \cr} \right)\) means translate the shape 4 squares to the right and 3 squares down.
\(\left( \matrix{-2 \cr 1 \cr} \right)\) means translate the shape 2 squares to the left and 1 square up.
Vectors are given in the form \(\binom{x}{y}\) where \(x\) is the movement horizontally and \(y\) is the movement vertically. A positive value of \(x\) means a movement to the right and a negative value of \(x\) means a movement to the left. A positive value of \(y\) means a movement upwards and a negative value of \(y\) means a movement downwards.
Example
Solution:
Triangle PQR has been translated 4 squares right and 3 squares down.This would be described as a translation by the vector \(\left( \matrix{ 4 \cr -3 \cr} \right)\)

There will be a mark for writing translation and a mark for writing (\(\left( \matrix{ 4 \cr -3 \cr} \right)\)
Example
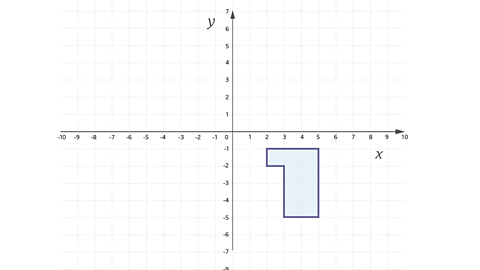
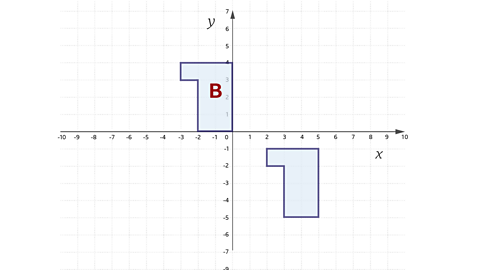
Translate the shape using the vector \(\left( \matrix{ 5 \cr -5 \cr} \right)\) and label it B.
Solution
The shape will be moved 5 to the left and 5 up.
Reflection
When a shape is reflected it is flipped. The line of reflection could be the x axis or the y axis or a line parallel to either axis that is a horizontal or vertical line.
To reflect a shape
- Draw the line of reflection.
- Choose a point on the shape and count how far it is from the line of reflection.
- Count the same amount on the other side of the line and plot the point.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each point in the shape and join the points.
Example
Reflect the shape in the line x = -1
Solution:
- Draw the line of reflection.
The line x= -1 is a vertical line which passes through -1 on the x axis. - Choose a point on the shape and count how far it is from the line of reflection.
The line is across 2 squares from A - Count the same amount on the other side of the line and plot the point.
The reflection of A is 2 squares to the left of the reflection line. - Repeat steps 1 and 2 for each point in the shape and join the points.
Question
Describe the transformation of the shape ABC.
Answer:
The line y = 1 is a horizontal line which passes through 1 on the y-axis.
The shape has been reflected in the line y = 1.
Remember
There will be a mark for writing reflection and a mark for writing in the line y = 1
Question
Describe the transformation which maps shape S to shape T.
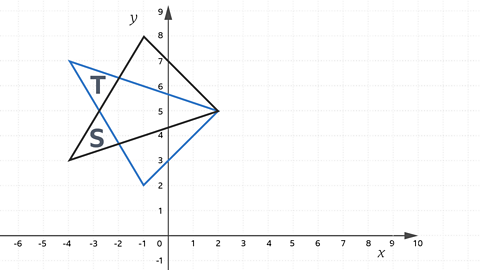
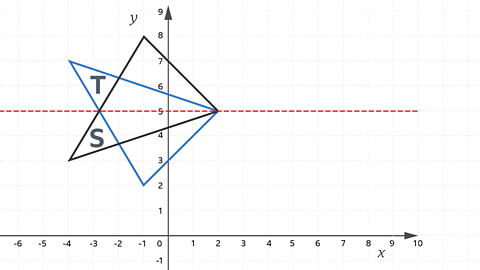
A reflection in the line y = 5
Rotation
When a shape is rotated it is turned about a fixed point, the centre of rotation.
Three pieces of information are necessary to rotate a shape:
- The centre of rotation, at M6 this could be anywhere on the grid.
- The angle of rotation, 90° or 180°
- The direction of rotation, clockwise CW or anticlockwise ACW.
You can use tracing paper to help.
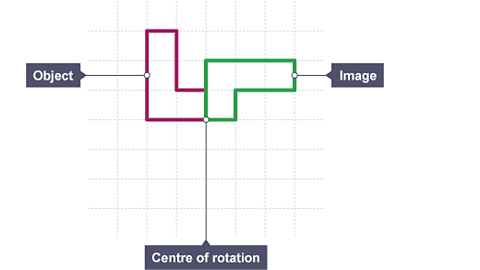
Image caption, The shape has been rotated 90° (a quarter turn) clockwise about the centre of rotation
Image caption, The shape has been rotated 180° (a half-turn) about the centre of rotation
Image caption, The shape has been rotated 90° (a quarter turn) anticlockwise about the centre of rotation
1 of 3
How to rotate a shape using tracing paper.
Hold down the tracing paper with a pencil on the centre of rotation.
Rotate the tracing paper and copy the image.
Different centres of rotation
The centre of rotation may not be at the origin (0,0).
Rotate the rectangle ABCD 90° clockwise about the point (0,-1).
Each corner of the image A'B'C'D' is the same distance from the centre of rotation as the original shape.
Enlargement
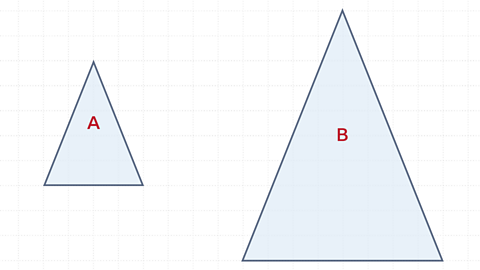
The base of A is 4 and the height is 5.
The base of B is 8 and the height is 10.
Shape B is an enlargement of shape A with scale factor 2.
Effect of Enlargement on Perimeter and Area
Example
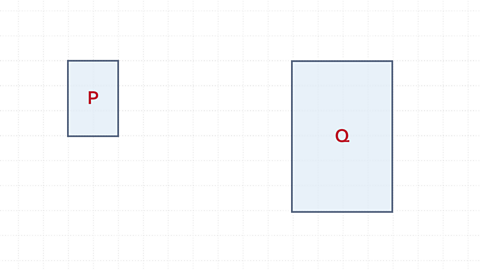
The perimeter of rectangle P is 10
The perimeter of rectangle Q is 20
The perimeter has also been enlarged by scale factor 2
This is because perimeter is a length.
The area of P is 2 x 3 = 6 squares
The area of Q is 4 x 6 = 24 squares.
The area has been enlarged by scale factor 4.
This is the length scale factor squared because the sides are multiplied. 2² = 4
Example
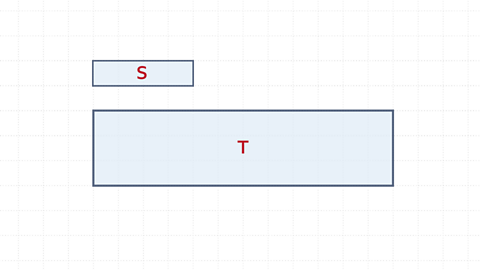
The perimeter of rectangle S is 10
The perimeter of rectangle T is 30
The perimeter has also been enlarged by scale factor 3
This is because perimeter is a length.
The area of S is 1 x 4 = 4 squares
The area of T is 3 x 12 = 36 squares.
The area has been enlarged by scale factor 9.
This is the length scale factor squared because the sides are multiplied. 3² = 9
Test yourself
More on M6: Geometry and measures
Find out more by working through a topic