How is electricity generated?
Electricity comes from a wide range of sources but have you ever wondered how that electricity is made?
In this article you can learn about:
- Different energy sources used to make electricity
- How turbines and generators generate electricity
- How electricity gets to our homes and schools
This resource is suitable for energy and sustainability topics for primary school learners.
Video - Generating electricity
Learn where electricity comes from and how generators work in this fun short video.
We use electricity every day for hundreds of different things.
But where does it come from?
Well, electricity is made from lots of sources of energy…
Like sun rays that charge solar panels. Or rushing water in a hydro dam. Or tides and waves in the sea. Or smelly gases from household waste. Or fossil fuels that we burn. Or geothermal heat from underground pools. Or wind that turns turbines, or- hang on a second…
What are you doing?
Trying to charge your phone directly from the wind?
Look, we can't get electricity straight from sources of energy.
There's a step in between.
The most common way of making electricity is by using energy to turn turbines, like the way the kinetic energy of the wind blows wind turbines around.
If you want to convert that kinetic energy into electricity, the turbines need to be connected to a clever bit of kit called a generator.
So, how does a generator work?
Inside the generator is a ring of magnets and around this is lots of coiled up metal wire. The wind spins the turbine and this spins the magnets, and the spinning magnets generate an electrical current that flows through the wires. The faster the magnets spin, the more electricity is produced!
Not all electricity starts with kinetic energy.
Gas power plants start with chemical energy - burning gas and hot air to turn turbines. And solar panels don't use turbines at all! They convert energy from the sun directly into electricity.
But however electricity is produced, it needs to be transported to houses. This is done through power lines. Then it transfers to underground cables or smaller power lines and then it goes to your home!
So, next time you flick the switch on your bedside light, just think about the journey your electricity has been on.
Nighty-night!
Where does electricity come from?
Electricity comes from a wide range of sources - solar panels, hydroelectric dams, geothermal reservoirs, fossil fuels, gases from our waste and even the energy stored inside atoms can all be used to generate electricity.
We don’t get electricity directly from these sources. There is a process between capturing energy from the wind or sun or chemicals and plugging in a device to supply it with the electricity it needs to work.
How is electricity made?

Most of the ways we generate electricity involve kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving gases or liquids can be used to turn turbines:
- Wind turbines are turned by moving air.
- Hydroelectric turbines are turned by water flowing down through pipes.
- Wave and tidal turbines are turned by the movement of the sea.
Other energy sources start with heat energy. Geothermal, nuclear, biomass and fossil fuel power stations all produce heat. This heat energy is used to heat water into steam, or to heat other liquids or gases.
Heating liquids or gases makes them expand and take up more room. This causes movement that can be used to turn turbines.

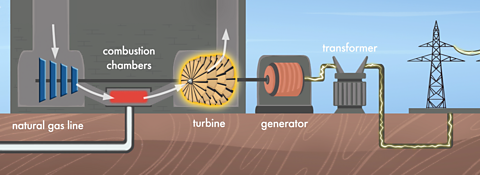
What is inside a generator?

In power stations, turbines are connected to generators. Inside the generator is a ring of magnets and this is surrounded by another ring, made up of lots of tightly wrapped metal wire.
When the generator turns, the magnets spin round. The movement of magnets past the wires makes electricity start to flow through the wires.

How is electricity transported?
Electricity is transported via our National Grid of power lines and cables. Some of these cables have large pylons in fields. Others are underground and connected to homes and buildings.

Electricity facts
9.5% of the world’s population (740 million people) have no access to electricity. In comparison, people in the UK power many different devices and machines using electricity every day.
Some electricity is created from non-renewable sources, like fossil fuels. These fossil fuels produce carbon emissions that contribute to climate change and will eventually run out.
Some electricity is created from renewable sources, like wind or hydroelectricity which are climate friendly and won’t run out.
Electricity is not a human creation. It is present in many natural processes as well, such as how our hearts beat, how thunderstorms cause lightning and even how electric eels can shock their prey.

Key words about generating electricity
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Solar panels are used to produce electricity. Made from lots of solar cells, solar panels can be found on buildings but can also be used on a solar farm to harvest the power of the sun.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - Kinetic energy is energy that an object possesses because of its movement. The kinetic energy of the wind or water can turn the blades on a turbine to generate electricity.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - A simple turbine has a shaft and blades that turn movement of liquids or gases into mechanical movement. Usually, water or air push the blades and turn the shaft. Turbines are used to turn the generator.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A machine that is used to make electricity. When the generator head is turned, this kinetic energy is converted to electrical energy.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. - The National Grid is the name given to the network of pylons and powerlines that transport electricity to our homes, schools, offices and businesses.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Large metal structures that hold electric cables high above the ground, away from people, animals or obstructions.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Challenge

Have a look around you
As you go about your day, can you spot any of the different parts of the process of creating and transporting electricity?
Here is a checklist of things to look for:
- Wind farms or solar panels
- A power station
- A power substation on a street
- An electricity pylon
- Cables carrying electricity
- Plug sockets in a home or building
Important! Electricity can be dangerous! Do NOT touch plug sockets or attempt to touch power lines or cables or attempt to go into power stations or substations. This task is only about looking and is best done with an adult for guidance. Look out for, and pay attention to, any warning signs around electricity and electrical devices.
More on Energy sources and sustainability
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 14

- count5 of 14

- count6 of 14

- count7 of 14
