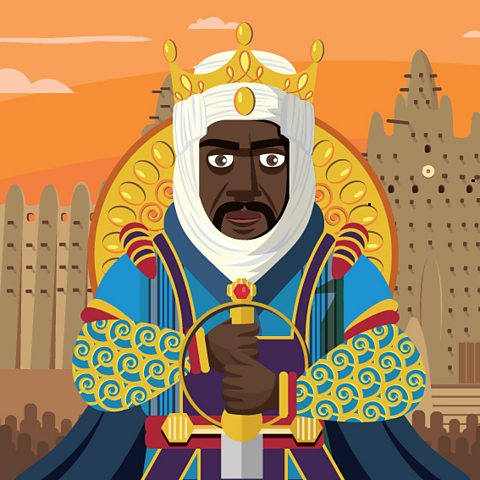
Kingdoms in West Africa through time

West Africa has been home to some great kingdoms and empires.
The earliest of these kingdoms belonged to the Nok people. They were farmers, potters and metalworkers who settled near the River Niger around 500BC.
The kingdom of Ife developed in the rainforest in the 600s.
Its art and religion influenced the culture of Benin, which began in the 900s and reached the height of its power between the 1400s and the 1600s.

Between 700 and 1600 there were three great empires in the centre of West Africa: Ancient Ghana, Mali and Songhai. They all grew immensely rich by trading in gold.
One of the last great kingdoms was Asante. It was founded around 1700. The Asante people were famous for their work in gold.
What kind of art did people create?
The people of West Africa were skilled potters and metalworkers. Some of them worked with brass and some with gold.
Potters in the kingdom of Nok made sculptures from a type of clay called terracotta. They created figures of people. Many of the figures had elaborate hairstyles and wore delicate jewellery.

The kingdom of Ife was famous for its sculptures made from brass. Brass-workers made figures of gods, humans and animals.
In the Asante kingdom, goldsmiths made ornaments to show off the wealth of their king. The king wore golden necklaces, rings, bracelets and anklets.
He even had a pair of gold castanets attached to his thumb and first finger. The king clapped the castanets together when he wanted people to listen to him!
Who was Mansa Musa?
Mansa Musa was a wealthy Muslim king of Mali. He ruled from around 1280 to 1340.
Mansa Musa travelled to the Muslim holy city of Mecca with a procession of 72,000 men carrying gold. He also took 80 camels loaded with sacks of gold dust. Musa gave away gold to people he met on his route.
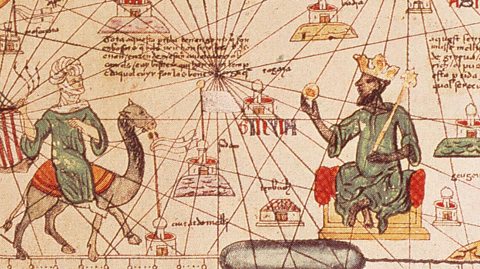
Mansa Musa brought back teachers and architects from his travels to Mali.
He built many mosques and schools in the cities of Timbuktu and Gao. The buildings had colourful domes and their doors and windows were covered with gold.
Some of these buildings survive in Timbuktu today, but they have lost their golden decorations.
Listen: Ibn Battuta's travels
In 1352, an Arab traveller called Ibn Battuta visited Mali. He arrived at the city of Niani where Mansa Suleyman, grandson of Mansa Musa, had his palace. Suleyman was not a great ruler like Musa, but he lived in style! Find out what Ibn Battuta saw.
I had a wretched journey across the Sahara desert. Only the thought of the famous kingdom of Mali kept me going. I had heard great stories about the land of gold and I knew I had to see it with my own eyes.
Just then as I arrived in the kingdom of Mali, I very nearly died! I ate some rotten yams that made me so sick I had to take to my bed. It was two whole months before I had the strength to visit the royal palace.
As I reached the palace gates I saw around 300 slaves, some armed with bows and some with lances - all of them devoted to the service of their king, Mansa Suleyman. Then I was led to the vast council hall where the king received his visitors.
No one was allowed to approach the king directly. Instead I sat with chiefs and warriors and visitors of all kinds. We waited in a broad avenue lined with trees, for our turn to send a message.
When I finally took my turn, I had to speak through an Interpreter. He was a splendid figure in silken robes wearing a turban with elaborate fringes. Then the Interpreter spoke to a man who stood near the king and that man finally gave my message tothe king.
On another day, I attended a festival in honour of the king. I saw a parade of chiefs all riding on horseback, with their followers carrying weapons and playing drums and bugles. There were other musicians with instruments made from reeds and gourds, which they beat with sticks to make a wonderful sound.
The Interpreter sat on a special chair and sang loudly in praise of his king. He was joined by a choir of women and pages, and then came the acrobats and jugglers with swords.
When I finally got to see Mansa Suleyman, he gave me a strange gift - a small dish of bread, meat and yogurt. Later I complained to him, telling him of all the generous rulers I had met on my travels. After that, he offered me a house where I could stay and when I left his country he gave me gifts of gold.
I shall never forget my visit to Mali however long I live.
What happened to the African kingdoms?

Most West African kingdoms slowly came to an end. Then new African kingdoms grew up to take their place.
However, some kingdoms were taken over by European countries.
By the 1890s, many countries in Europe were competing for land in Africa. They wanted to gain control of valuable trading goods, such as gold, oil and rubber. Britain and France both wanted land in West Africa.

Most West African kingdoms slowly came to an end. Then new African kingdoms grew up to take their place.
However, some kingdoms were taken over by European countries.
By the 1890s, many countries in Europe were competing for land in Africa. They wanted to gain control of valuable trading goods, such as gold, oil and rubber. Britain and France both wanted land in West Africa.

Activities
Activity 1: Map of West Africa
Explore the map below to find out more about the kingdoms of West Africa.
Activity 2: Quiz – Kingdoms of West Africa
Bitesize Primary games. gameBitesize Primary games
Play fun and educational primary games in science, maths, English, history, geography, art, computing and modern languages.

More on Kingdom of Benin
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 8

- count6 of 8

- count7 of 8

- count8 of 8
