Human Cells
Division and differentiation in human cells
When cells express specific genes that characterise a certain type of cell we say that a cell has become differentiated.
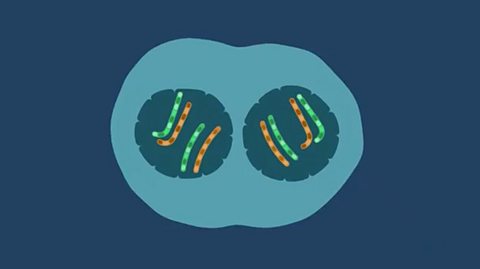
Structure and replication of DNA
DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for all living things. DNA achieves this feat of storing, coding and transferring biological information though its unique structure.

Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which specific genes are activated to produce a required protein. The process is made up of the transcription and translation of DNA sequences.
Genome and mutations
DNA replication is carefully controlled to preserve the genetic information. However, changes in the genome do sometimes occur. These changes are known as mutations.
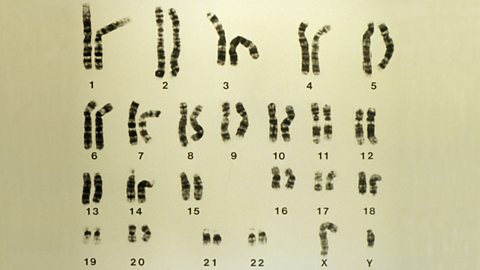
Human genomics
The human genome is made from DNA. The gene portion codes for proteins and non-coding sections control the expression of genes. An individual’s genetic code is unique.

Metabolic pathways
Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions that take place inside living cells. Unicellular and multicellular organisms must control their metabolism in order to survive.

Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration refers to the breakdown of glucose and other respiratory substrates to make energy carrying molecules called ATP.

Energy systems in muscle cells
During exercise when muscles do not get enough oxygen, lactate is produced. After exercise oxygen dept must be repaid. Slow-twitch muscles rely on aerobic respiration. Fast-twitch fibres generate ATP through glycolysis only.
