Right-angled triangles
Pythagoras' theorem states that for all right-angled triangles:
The square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
The hypotenuse is the longest side and it's always opposite the right angle.
In this triangle \(a^2 = b^2 + c^2\) and angle \(A\) is a right angle.
Pythagoras' theorem only works for right-angled triangles, so you can use it to test whether a triangle has a right angle or not.
In the triangle above, if \({a}^{2}~\textless~{b}^{2}+{c}^{2}\) the angle \(A\) is acute.
In the triangle above, if \({a}^{2}~\textgreater~{b}^{2}+{c}^{2}\) the angle \(A\) is obtuse.
Question
Which of the following triangles is right-angled?
a)
b)
c)
Answer a)
\(8^2 = 64\)
\(5^2 + 6^2 = 25 + 36 = 61\)
\(8^2\) is greater than \(5^2 + 6^2\), so angle \(A\) must be obtuse.
Answer b)
\(13^2 = 169\)
\(5^2 + 12^2 = 25 + 144 = 169\)
\(13^2\) is equal to \(5^2 + 12^2\) so angle \(P\) must be a right angle.
Answer c)
\(10^2 = 100\)
\(5^2 + 9^2 = 25 + 81 = 106\)
\(10^2\) is less than \(5^2 + 9^2\) so angle \(X\) must be acute.*
So, it is triangle b which is right-angled.
Working out the hypotenuse
Question
Work out the length of the line \({BR}\), correct to \({1}\) decimal place.
Answer
\(BR^2 = 4^2 + 7^2\)
\(BR^2 = 16 + 49\)
\(BR^2 = 65\)
\({BR}=\sqrt65\) (Find the square root of both sides) \(BR={8.1~cm}\) (\({1}\) decimal place)
Calculating the length of another side of a triangle
If you know the length of the hypotenuse and one of the other sides, you can use Pythagorasâ theorem to find the length of the third side.
We can rearrange the formula for Pythagorasâ theorem, in order to make \({b}\) or \({c}\) the subject of the formula:
\({a}^{2}={b}^{2}+{c}^{2}\)
\({b}^{2}={a}^{2}-{c}^{2}\)
\({c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}\)
Example
Work out the length of the line \({LM}\), correct to \({1}\) decimal place.
\({LM}^{2}={LN}^{2}-{MN}^{2}\)
\({LM}^{2}={6}^{2}-{4}^{2}\)
\({LM}^{2}={36}-{16}\)
\({LM}^{2}={20}\)
\({LM}=\sqrt{20}\)
\({LM}={4.5~cm}\) (\({1}\) decimal place)
Question
Work out the length of the line \(YZ\), correct to \({1}\) decimal place.
Answer
Method 1
\({YZ}^{2}+{XZ}^{2}={XY}^{2}\)
\({YZ}^{2}+{7}^{2}={8}^{2}\)
\({YZ}^{2}+{49}={64}\)
\({YZ}^{2}={15}\) (subtract \({49}\) from both sides)
\({YZ}=\sqrt{15}\) (find the square root of both sides)
\({YZ}={3.9~cm}\) (\({1}\) decimal place)
Method 2
\({YZ}^{2}={XY}^{2}-{XZ}^{2}\)
\({YZ}^{2}={8}^{2}-{7}^{2}\)
\({YZ}^{2}={64}-{49}\)
\({YZ}^{2}={15}\)
\({YZ}=\sqrt{15}\) (find the square root of both sides)
\({YZ}={3.9~cm}\) (\({1}\) decimal place)
Length of a line segment
You can also use Pythagoras' theorem to find the distance between two points:
Determining distance with Pythagoras' theorem
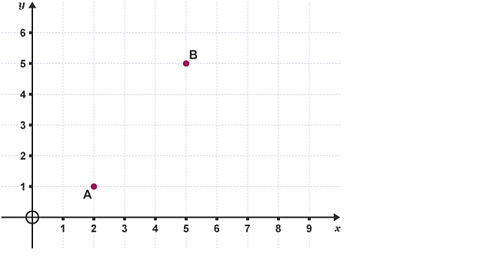
Image caption, A is located at the point (2, 1). B is located at the point (5, 5).
Image caption, A and B are connected
Image caption, Triangle width and height are marked
Image caption, Distance of AB is calculated
1 of 4
Test section
Question 1
Is a triangle with sides of \({3}~{cm}\), \({4}~{cm}\) and \({5}~{cm}\) a right-angled triangle?
Answer
Yes, it is.
âThe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
In this case \({5}^{2}={3}^{2}+{4}^{2}\).
Question 2
Is a triangle with sides of \({5}~{cm}\), \({6}~{cm}\) and \({12}~{cm}\) a right-angled triangle?
Answer
No, it's not.
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
In this case \({12}^{2}\neq{5}^{2}+{6}^{2}\).
Question 3
What is the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle when the lengths of the other sides are \({6}~{cm}\) and \({8}~{cm}\)?
Answer
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
So the \({hypotenuse}^{2}={6}^{2}+{8}^{2}={100}\).
Therefore the \({hypotenuse}=\sqrt{100}={10}~{cm}\).
Question 4
What is the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle when the lengths of the other sides are \({5}~{cm}\) and \({9}~{cm}\)?
Answer
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
So the \({hypotenuse}^{2}={5}^{2}+{9}^{2}={106}\).
Therefore the \({hypotenuse}=\sqrt{106}={10.3}~{cm}~(1~dp)\).
Question 5
What is the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle when the lengths of the other sides are \({6}~{m}\) and \({12}~{m}\)?
Answer
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides'.
So the \({hypotenuse}^{2}={6}^{2}+{12}^{2}={180}\).
Therefore the \({hypotenuse}=\sqrt{180}={13.4}~{m}~(1~dp)\).
Question 6
What is the length of one side of a right-angled triangle when the length of the hypotenuse is \({10}~{cm}\) and the length of the other side is \({4}~{cm}\)?
Answer
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
\({x}={length~of~side}\)
So \({10}^{2}={x}^{2}+{4}^{2}\), \({x}^{2}={10}^{2}-{4}^{2}={84}\)
\({x}=\sqrt{84}={9.2}~{cm}~(1~dp)\).
Question 7
What is the length of one side of a right-angled triangle when the length of the hypotenuse is \({18}~{cm}\) and the length of the other side is \({10}~{cm}\)?
Give your answer correct to \({1}\) decimal place.
Answer
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
\({x}={length~of~side}\)
So \({18}^{2}={x}^{2}+{10}^{2}\)
\({x}^{2}={18}^{2}-{10}^{2}={224}\)
\({x}=\sqrt{224}={15.0}~{cm}~(1~dp)\).
Question 8
What is the length of one side of a right-angled triangle when the length of the hypotenuse is \({20}~{mm}\) and the length of the other side is \({14}~{mm}\)?
Answer
Remember that âthe square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sidesâ.
\({x}={length~of~side}\)
So \({20}^{2}={x}^{2}+{14}^{2}\)
\({x}^{2}={20}^{2}-{14}^{2}={204}\)
\({x}=\sqrt{204}={14.3}~{mm}~(1~dp)\).
Question 9
\({A}\) is located at \(({1},~{2})\), and \({B}\) is located at \(({5},~{6})\).
What is the length of \({AB}\)?
Answer
Note that the width of the triangle is \({4}~{units}\) (\({x}\)-coordinates: \({5}-{1}={4}\)) and the height of the triangle is \({4}~{units}\) (\({y}\)-coordinates: \({6}-{2}={4}\)), so the \({length~of~the~hypotenuse}=\sqrt({4}^{2}+{4}^{2})={5.7}~{units}~(1~dp)\).
Question 10
\({X}\) is located at \(({3},~{1})\), and \({Y}\) is located at \(({6},~{4})\).
What is the length of \({XY}\)?
Answer
Note that the width of the triangle is \({3}~{units}\) (\({x}\)-coordinates: \({6}-{3}={3}\)) and the height of the triangle is \({3}~{units}\) (\({y}\)-coordinates: \({4}-{1}={3}\)), so the \({length~of~the~hypotenuse}=\sqrt({3}^{2}+{3}^{2})={4.2}~{units}~(1~dp)\)
More on Shape, space and measures
Find out more by working through a topic
- count29 of 52

- count30 of 52
- count31 of 52
- count32 of 52
