Key points
The areaA measure of the size of any plane surface or 2D shape. Area is measured in square units, for example, square centimetres or square metres: cmÂČ or mÂČ. is the total area of all the faceOne of the flat surfaces of a solid shape. of the shape. For example, the surface area of a cube is the total area of all six square faces. This is 6 Ă sideÂČ.
Surface area is measured in square units including cmÂČ and mÂČ.
The edgeThe line formed by joining two vertices of a shape. The line formed when two faces meet. of the square is the edge of the cube and is the length, width and height dimensions of the 3D shape.
A cuboidA 3D shape with six rectangular faces. The opposite faces are congruent. has six faces and opposite pairs of faces are congruentShapes that are the same shape and size, they are identical.. The dimensionThe length, width, height or depth of something. of a cuboid are paired to give three congruent pairs of faces. For example, a cuboid with dimensions 2 cm Ă 3 cm Ă 4 cm has two faces which measure 2 cm Ă 3 cm, two which measure 2 cm Ă 4 cm and two which measure 3 cm Ă 4 cm.
The netA group of joined 2D shapes which fold to form a 3D shape. of a 3D shape is what a shape looks like when it is opened out into a 2D shape. The net can help to show the areas of each face that make up the surface area of a shape.

Calculating the surface area of a cube
A cube has six congruent square faces. The total area of the faces is the surface area of the cube.
To work out the surface area of a cube:
- square (verb)Multiply a number by itself. one edge of the cube. This gives the area of one square face.
- Multiply the area of one square face by six.
To find the length of an edge of a cube:
- Divide the total surface area by six. This gives the area of one square face.
- Find the square root âA value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number. Eg, 4 Ă 4 = 16, so the square root of 16 is 4. â16 = 4.
Examples
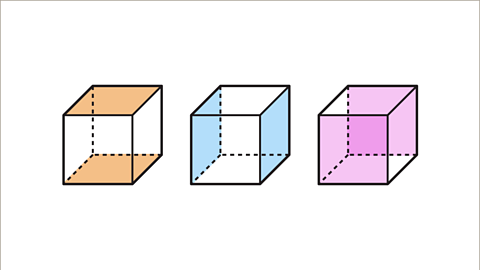
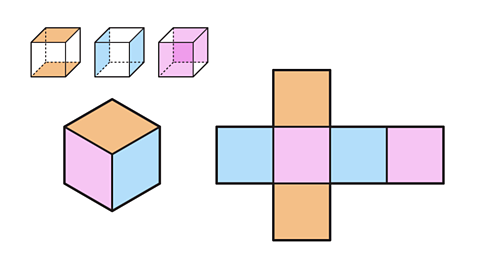
Image caption, A cube has six faces. Each face of a cube is a square.
Image caption, A net shows all the faces of the cube.
Image caption, Where đ is the length of one edge of the cube, the area of one square face is đÂČ. The total surface area of the cube is 6đÂČ.
Image caption, The cube has a side length of 3 cm. Work out the surface area of the cube.
Image caption, Find the area of one face. The face is a square. The area of the square face is the side length multiplied by itself (squared). 3ÂČ = 9. The area of one face of the cube is 9 cmÂČ.
Image caption, The total surface area of the cube is the area of all six faces. 6 Ă 9 = 54. The total surface area of a cube with side lengths of 3 cm is 54 cmÂČ.
Image caption, The total surface area of a cube is 486 cmÂČ. What is the length of an edge of the cube?
Image caption, The surface area of the cube is 6 Ă area of one face. Find the area of one face by dividing the surface area by 6. 486 Ă· 6 = 81. The area of one square face of the cube is 81 cmÂČ.
Image caption, Find the length of an edge of the cube by finding the square root of the area of a square face. â81 = 9. The edge of the cube is 9 cm.
1 of 9
Question
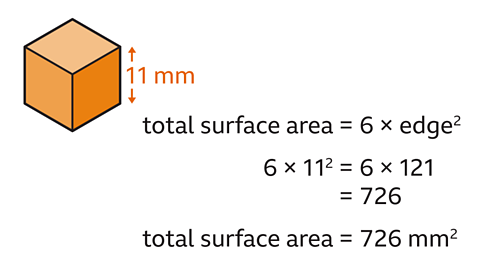
What is the total surface area of a cube with an edge of 11 mm?
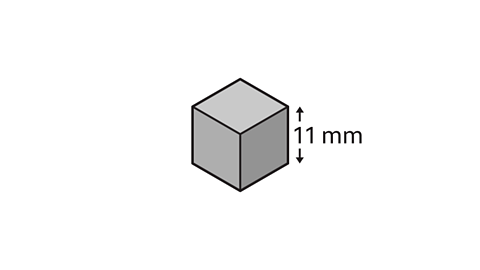
The surface area of a cube is 6 Ă area of a square face = 6 Ă edgeÂČ
6 Ă 11ÂČ = 726
The surface area of the cube is 726 mmÂČ.
Calculating the surface area of a cuboid
A cuboid has three pairs of congruentShapes that are the same shape and size, they are identical. faces:
- The top face and the base face.
- The left and right faces.
- The front and back faces.
To work out the total surface area of a cuboid:
- Find the area of the top and base faces. This is length Ă width Ă 2
- Find the area of the right and left faces. This is width Ă height Ă 2
- Find the area of the front and back faces. This is length Ă height Ă 2
- Add the face areas to find the total surface area.
The formula for the surface area of a cuboid with the dimensions đ Ă đ Ă đ can be given as:
Surface area = 2đđ + 2đđ + 2đđ or surface area = 2(đđ + đđ + đđ).
Examples
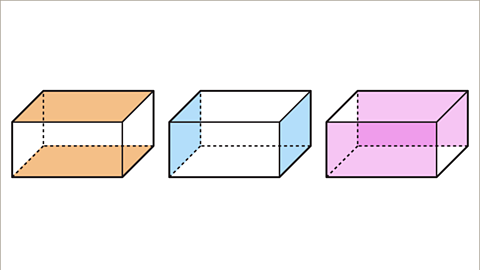
Image caption, A cuboid has three pairs of congruent faces. The top and base faces are congruent. The left and right faces are congruent. The front and back faces are congruent.
Image caption, A net of a cuboid shows that the opposite faces are congruent. The top and base faces are congruent. The left and right faces are congruent. The front and back faces are congruent.
Image caption, Find the total surface area of the cuboid. The length is 6 cm, the width is 4 cm and the height is 3 cm.
Image caption, Find the area of the top and base faces. This is length Ă width Ă 2. 6 Ă 4 Ă 2 = 48. The area of the top and base faces is 48 cmÂČ. Find the area of the right and left faces. This is width Ă height Ă 2. 4 Ă 3 Ă 2 = 24. The area of the right and left faces is 24 cmÂČ. Find the area of the front and back faces. This is length Ă height Ă 2. 6 Ă 3 Ă 2 = 36. The area of the front and back faces is 36 cmÂČ.
Image caption, To find the total surface area, add together the face areas. 48 + 24 + 36 = 108. The total surface area of the cuboid is 108 cmÂČ.
Image caption, The calculation for the surface area of a cuboid can be expressed as a formula. The formula is 2đđ + 2đđ + 2đđ where đ is the length, đ is the width and đ is the height. Use the formula to find the total surface area of a cuboid with length 18 cm, width 10 cm and height 4 cm.
Image caption, Substitute the values for the length, width, and height into the formula for the surface area of a cuboid. The calculation is 2 Ă 18 Ă 10 + 2 Ă 10 Ă 4 + 2 Ă 18 Ă 4
Image caption, 2 Ă 18 Ă 10 + 2 Ă 10 Ă 4 + 2 Ă 18 Ă 4 = 584. The formula calculates the areas of the top and base faces, the right and left faces, and the front and back faces. The total surface area of the cuboid is 584 cmÂČ.
Image caption, The formula for the surface area of a cuboid can be expressed in a different form, surface area = 2(đđ + đđ + đđ) where đ is the length, đ is the width and đ is the height. The calculation 2(18 Ă 10 + 10 Ă 4 + 18 Ă 4) gives the same answer. The total surface area of the cuboid is 584 cmÂČ.
1 of 9
Question
Find the total surface area of the cuboid.
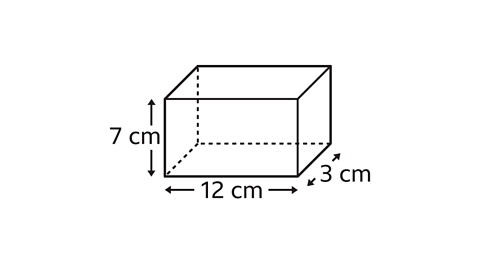
The dimensions of the cuboid are length 12 cm, width 3 cm and height 7 cm.
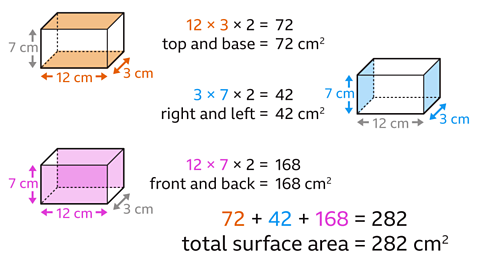
Work out the area of the top and base faces (length Ă width Ă 2).
12 Ă 3 Ă 2 = 72. The area of the top and base faces is 72 cmÂČ.
Work out the area of the right and left faces (width Ă height Ă 2).
3 Ă 7 Ă 2 = 42
The area of the left and right faces is 42 cmÂČ.
Work out the area of the front and back faces (length Ă height Ă 2).
12 Ă 7 Ă 2 = 168
The area of the front and back faces is 168 cmÂČ.
Find the total of the areas of all faces.
72 + 42 + 168 = 282
The total surface area of the cuboid is 282 cmÂČ.
Practise finding the surface area
Practise finding the surface area of cubes and cuboids with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Quiz
Game - Divided Islands
Play the Divided Islands game! gamePlay the Divided Islands game!
Using your maths skills, help to build bridges and bring light back to the islands in this free game from ±«Óătv Bitesize.

More on Perimeter, Area, Volume
Find out more by working through a topic
- count9 of 11
- count10 of 11
- count11 of 11
- count1 of 11