Key points
- Days, years and months are periods of time which are determined by the movement of Earth around the Sun, and the movement of the Moon around Earth.
- The Earth’s axis of rotation The imaginary line through the centre of the Earth between the South and North poles which the Earth rotates around. This axis is tilted compared to the angle the Earth orbits the Sun. is tilted, which leads to changing seasons as Earth itself orbitThe path an object takes through space when it moves around a star, planet or moon. Objects are held in orbit by the force of gravity. around the Sun.
Days and nights
- As Earth orbits the Sun, it rotates on its axisThe imaginary line running through the Earth from the North to the South pole on which the Earth rotates. The axis is tilted at 23.4°. . Each rotation of Earth on its axis takes 24 hours. This period of time is called a dayThe time it takes for a planet to rotate once on its axis. On Earth, a day is 24 hours long..
- As Earth rotates on its axis, the side of Earth facing towards the Sun is lit by the Sun. People living on this side of the Earth experience day.
- The opposite side of Earth at this point is facing away from the Sun and people living on this side experience night.
Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted, as you can see from this illustration. This means that day and night are not equal lengths in most places on the planet.
Years and seasons
Earth takes approximately 365 days to orbit once around the Sun. This length of time is called a yearA planet's year is the time it takes to make one complete orbit around the Sun. The Earth goes once round the Sun in one Earth year, which takes 365 Earth days. .
As Earth moves through its orbit around the Sun, different parts of the planet are tilted closer or further from the Sun, because of the tilt in Earth’s axis.
It is the angle of the Earth's tilt that causes the seasons: spring, summer, autumn and winter.
When the axis is tilted towards the Sun, that hemisphereHalf of a sphere shape. Dividing the Earth into two halves. experiences summer. When the axis is tilted away from the Sun, that hemisphere experiences winter.
Watch this video to find out more about how the UK experiences seasons.
What are days, seasons and years ?
Consider a person living in the UK, which is in Earth’s northern hemisphere.It is summer in the UK when the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun.
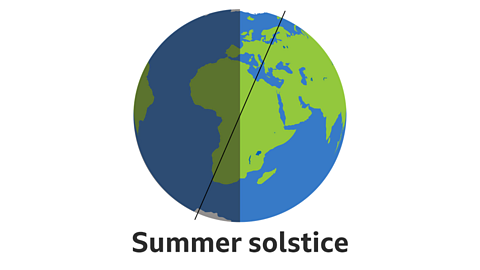
Image caption, The summer solstice, also known as midsummer, happens when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. In the northern hemisphere this takes place on 21 June.
Image caption, The winter solstice occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. In the northern hemisphere this takes place on 21 December.
1 of 2
In summer, daytime is longer than night-time and there are more hours of daylight. In regions near to the North Pole it is daylight 24 hours per day in summer.
When it is summer in the Northern HemisphereAny part of the Earth that lies to the north of the Equator., it is winter in the Southern HemisphereAny part of the Earth that lies to the south of the Equator.. When it is winter in the northern hemisphere, it is summer in the southern hemisphere.
Professor Brian Cox demonstrates how the orbit of the Earth results in days, nights and seasons, using an orange and a lamp
Why do we have day and night?
Why are the days longer in the summer and shorter in the winter here in the northern hemisphere?
And why do we have seasons?
Well, the answer has to have something to do with the sun, which is here, and the Earth, represented by this orange.
The answer lies in the way that the Earth spins on its axis - it goes round on its axis once a day.
And the way that it orbits around the sun - it goes round the sun once a year.
But the Earth is tilted - so, its spin axis is tilted, actually at an angle of around 23 degrees to the horizontal.
That means that - let's say this is northern hemisphere summer, so there's the North Pole - we're going to spin on our axis, but you see that the North Pole always gets sunlight, 24 hours a day. And if this is us, you see that this would be night, in the shadows, and the sun would rise about there, and the sun would be up, and sun would be up, and the sun would be up, and it'd be up, and it'd be up… and it would set around there.So in the summer, when the North Pole is pointing towards the sun, we get very short nights and very long days.
Then, let's go around six months, so the Earth goes halfway around the sun in its orbit. Now, the North Pole, which is here, is always pointing away from the sun. So, as the Earth spins, the sun never rises. It never shines on the North Pole.
Now we are there. And so, you see that we spend a very short amount of time in the daylight, lots of time in the shadows in the night, and not very long in the day.
So, in the winter, which is what this represents, the North Pole gets no sun at all. We get short days, a little bit of sunlight, and very long nights.
This, quarter way around again, would be the spring, back to the summer, the autumn and the winter.
So, the seasons occur because the Earth's axis is tilted and it goes around the sun - winter in the north, summer in the north.
And the days, because the Earth spins on its axis. It goes around once every, roughly 24 hours.
Why do we have leap years?
The time taken for Earth to orbit the Sun is actually closer to 365.25 days. This is why, every four years, we have a leap year. A leap year adds an extra day (29th February) to make up for the quarter days in Earth's orbit.
Months
A monthCalendar months are between 28 and 31 days in length. The length of a month is approximately equal to the time taken for the Moon to orbit Earth once. is measured by the time taken for the Moon to orbitThe path an object takes through space when it moves around a star, planet or moon. Objects are held in orbit by the force of gravity. Earth once.
The time for the Moon to go through a complete cycle (from a full Moon to the next full Moon) is approximately 29.5 days.
Calendar months are based on this and vary between 28 and 31 days in length.
Test your knowledge
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Space
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 9

- count5 of 9

- count6 of 9
