Reflex arc
Reflex actions
There are different types of neurones that work together in a reflex actionAutomatic and rapid response to a stimulus. .
This creates an automatic and rapid response to a stimulus, which minimises any damage to the body from potentially harmful conditions, such as touching something hot.
A reflex action follows this general sequence and does not involve the conscious part of the brain, which makes it much quicker.
The nerve pathway followed by a reflex action is called a reflex arcThe pathway of information from a sensory neuron through an inter neuron to a motor neuron.. For example, a simple reflex arc happens if we accidentally touch something hot.
- Receptor in the skin detects a stimulus (the change in temperature).
- Sensory neurone sends electrical impulses to relay neurone. Relay neurones are located in the spinal cord. They connect sensory neurones to motor neurones.
- Motor neurone sends electrical impulses to an effector.
- Effector produces a response (muscle contracts to move hand away).
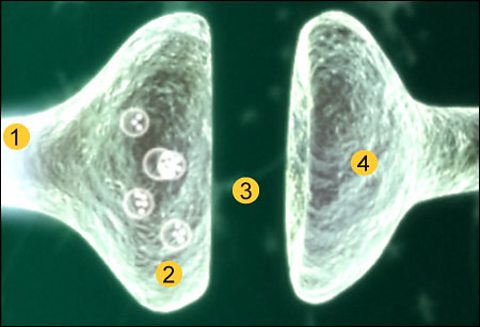
Where two neurones meet there is a small gap, a synapseA tiny gap at the junction between two nerve cells, which nerve signals must cross..
- An electrical impulse travels along the first axon.
- This triggers the nerve-ending of a neurone to release chemical messengers called neurotransmitterChemical involved in passing nerve impulses from one nerve cell to the next across a synapse..
- These chemicals diffuse across the synapse (the gap) and bind with receptor molecules on the membrane of the second neurone.
- The receptor molecules on the second neurone bind only to the specificneurotransmitters released from the first neurone. This stimulates the second neurone to transmit the electrical impulse.