Exam practice
GCSE Chemistry: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Chemistry past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.
GCSE Chemistry: exam-style questions
AQA Foundation and higher GCSE interactive tests based on past papers to get you ready for your chemistry exams. Topics include the periodic table, equations and more.

GCSE Chemistry: quick-fire questions
Use our interactive quiz to understand how the AQA foundation and higher chemistry GCSE exams work. Revise topics such as the periodic table and equations.

Quizzes
QUIZ: Atoms, elements and compounds
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying atoms, elements and compounds. Revise chemical symbols and chemical reactions.

QUIZ: Pure substances and mixtures
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying pure substances and mixtures. Test your knowledge of filtration, crystallisation and distillation.

QUIZ: Atomic structure
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying atomic structure. Test your knowledge of atomic models, atomic number and calculating atomic mass.
QUIZ: The periodic table
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying the periodic table. Test you knowledge of elements and Mendeleev’s early periodic table.

QUIZ: Groups in the periodic table (activity 1)
his interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying the periodic table. Test your knowledge of where the different groups are in the periodic table.

QUIZ: Groups in the periodic table (activity 2)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying the periodic table. Test you knowledge of chemical and physical properties and chemical reactions.

QUIZ: Transition metals
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying transition metals. Revise the physical and chemical properties of transition metals.

QUIZ: Reactions of metals
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying the reactions of metals. Test your knowledge of the reactivity series and the extraction of metals.

QUIZ: Acids, alkalis and salts (1)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying acids, alkalis and salts. Test your knowledge on neutralisation, reactions with acids and solutions.

QUIZ: Acids, alkalis and salts (2)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying acids, alkalis and salts. Test your knowledge of indicators, reactions and chemical equations.

QUIZ: Titrations
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying titrations. Test your knowledge of titration calculations and making salts from acids and alkalis.

QUIZ: Electrolysis
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying Electrolysis. Electrolysis involves using electricity to break down electrolytes to form elements.
QUIZ: The three states of matter
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying the three states of matter. Test your knowledge on the properties of substances and changes of state.

QUIZ: Ionic compounds
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying ionic compounds. An ionic compound is made up of charged particles, called ions.

QUIZ: Small molecules
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying small molecules. Test you knowledge of covalent bonds, electrons and atoms.

QUIZ: Giant covalent molecules
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying giant covalent molecules.Giant covalent substances have many atoms joined together by covalent bonds.

QUIZ: Metals and alloys
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying metals and alloys. Test your knowledge on structure and bonding in metals and how alloys are made.

QUIZ: Nanoscience
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying nanoscience. Answer questions about nanoparticles and the properties of Nanoparticulate materials.
QUIZ: Crude oil, hydrocarbons and alkanes
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying crude oil, hydrocarbons and alkanes. Test your knowledge of fractional distillation and cracking.

QUIZ: Organic chemistry (1)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying organic chemistry. Test your knowledge of organic molecules, molecular formulae and their structures.

QUIZ: Organic chemistry (2)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying organic chemistry. Test your knowledge of carboxylic acids, polymerisation and amino acids.

QUIZ: Calculations in chemistry
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying calculations in chemistry. Test your knowledge of calculating relative formula mass.

QUIZ: Atom economy and gas calculations
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying atom economy, percentage yield and gas calculations.

QUIZ: Sustainable development
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying sustainable development. Test your knowledge of finite and renewable resources.

QUIZ: Water
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying water. Test your knowledge of potable water, desalination and waste water treatment.

QUIZ: Ways of reducing the use of resources
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying the ways of reducing the use of resources. Test your knowledge of the life-cycle assessment.
QUIZ: Using materials
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying using materials. Test your knowledge of corrosion, the uses of metals and composite materials.

QUIZ: Fertilisers
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying fertilisers. Test your knowledge of the Harber process and making ammonium.

Podcasts
Atomic structure and the periodic table
Learn about atomic structure and the periodic table for your GCSE chemistry exam, with Dr Sunayana Bhargava and Tulela Pea.

Bonding, structure and properties
Learn about bonding, structure and properties of matter for your GCSE chemistry exam, with Dr Sunayana Bhargava and Tulela Pea.

Chemical changes
Dr Sunayana Bhargava and Tulela Pea take you through what you need to know about chemical changes for your GCSE chemistry exam.

Science exam techniques
Learn all about science exam techniques for your GCSE science exams with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Atomic structure and the periodic table
Atoms, elements and compounds - AQA
Chemists use symbols and formulae to represent elements and compounds. Word equations and balanced chemical equations represent the changes that happen in chemical reactions.
Mixtures - AQA
There are different ways to separate mixtures, such as filtration, crystallisation, simple distillation, fractional distillation and chromatography. The method chosen depends on the type of mixture.

Atomic structure - AQA
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. The number of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated from the atom's atomic number and mass number.

The periodic table - AQA
Mendeleev made an early periodic table. In the modern periodic table, elements are in order of atomic number in periods and groups. Electronic structures model how electrons are arranged in atoms.

Groups in the periodic table - AQA
Elements in the same group of the periodic table show trends in physical properties, such as boiling point. They have the same number of electrons in their outer shell, so they are similar in their chemical properties.

Transition metals - AQA
The transition elements are metals. They have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. They form coloured compounds and act as catalysts.

Sample exam questions - atomic structure and the periodic table - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Bonding, structure and the properties of matter
The three states of matter - AQA
The three states of matter can be represented by the particle model. This model explains the properties of substances in their different states, as well as changes of state.
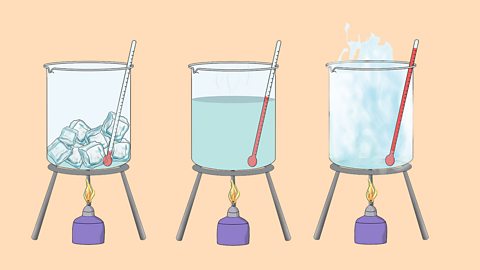
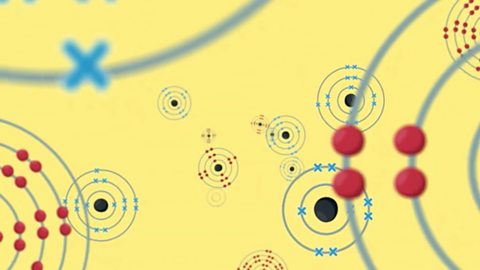
Ionic compounds - AQA
An ionic compound is made up of charged particles, called ions. It has a giant lattice structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction.

Small molecules - AQA
A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonding forms molecules. Substances with small molecules have low melting and boiling points, and do not conduct electricity.
Giant covalent molecules - AQA
Giant covalent substances have many atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Diamond, graphite and graphene are forms of carbon with different giant covalent structures.

Metals and alloys - AQA
The structure of metals explains their high melting and boiling points and their conductivity. The properties of a metal can be modified by mixing it with another substance to form an alloy.

Nanoscience - AQA
Nanoparticles are 1 nm to 100 nm in size. They have very large surface area to volume ratios. The properties of nanoparticulate substances are different from those of the same substance in bulk.

Sample exam questions - bonding, structure and matter - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Quantitative chemistry
Calculations in chemistry - AQA
Relative formula masses can be calculated and used in conservation of mass calculations. Calculations can be carried out to find out concentrations of solution and uncertainties in measurements.

Calculations in chemistry (Higher) - AQA
The mole is the unit for amount of substance. The number of particles in a substance can be found using the Avogadro constant. The mass of product depends upon the mass of limiting reactant.

Atom economy, percentage yield and gas calculations - AQA
Percentage yield and atom economy show how much desired product is obtained compared to amounts of starting materials. Gas calculations show volumes of gas used and obtained in chemical reactions.

Sample exam questions - quantitative chemistry - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Chemical changes
Reactions of metals - AQA
The reactivity series shows metals in order of reactivity. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive ions. Iron and aluminium are extracted from their ores in various ways.

Acids, alkalis and salts - AQA
Indicators are used to determine whether a solution is acidic or alkaline. Acids react with metals, bases and carbonates to produce salts. Neutralisation is the reaction between an acid and a base.

Titrations - AQA
The volumes of acids and alkali solutions that react with each other can be measured by titration using a suitable indicator.
Electrolysis - AQA
Electrolysis involves using electricity to break down electrolytes to form elements. The products of electrolysis can be predicted for a given electrolyte.

Sample exam questions - chemical changes - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Energy changes
Exothermic and endothermic reactions - AQA
Exothermic reactions transfer energy to the surroundings and the temperature of the surroundings increases. Endothermic reactions take in energy and the temperature of the surroundings decreases.

Chemical cells - AQA
A chemical cell produces a voltage until one of the reactants is used up. In a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, hydrogen and oxygen are used to produce a voltage, and water is the only product.

Sample exam questions - energy changes - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

The rate and extent of chemical change
Rates of reaction - AQA
The greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles, the greater the reaction rate.

Reversible reactions - AQA
Chemical reactions are reversible and may reach a dynamic equilibrium. The position of equilibrium of a reversible reaction can be altered by changing the reaction conditions.

Sample exam questions - the rate and extent of chemical change - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Organic chemistry
Crude oil, hydrocarbons and alkanes - AQA
Crude oil is a finite resource. Petrol and other fuels are produced from it using fractional distillation. Cracking is used to convert long alkanes into shorter, more useful hydrocarbons.
More organic chemistry - AQA
Alkanes, alkenes, alcohols and carboxylic acids are different homologous series of organic compounds. Naturally occurring and synthetic polymers can be formed from a variety of monomers.

Sample exam questions - organic chemistry - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple-choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Chemical analysis
Analysing and identifying substances - AQA
Formulations are complex mixtures of chemicals which have a specific use. Chromatography can be used to identify the substances present in a mixture of solutes.

Analysing substances - AQA
Flame tests and chemical tests are used to detect and identify ions in samples. Instrumental methods of analysis are faster, and more accurate and sensitive than simple chemical tests.

Sample exam questions - chemical analysis - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions. Arrangements for exam/non-exam assessments for students taking qualifications during the pandemic may be subject to change. Please check with your teacher.

Chemistry of the atmosphere
Developing the atmosphere - AQA
The early atmosphere was mainly carbon dioxide and water vapour. Water vapour condensed to form the oceans. Photosynthesis caused the amount of carbon dioxide to decrease and oxygen to increase.

Polluting the atmosphere - AQA
Human activities are causing global warming. Combustion of fuel produces many pollutants. Humans can reduce their impact on the environment.

Sample exam questions - chemistry of the atmosphere - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Using resources
Sustainable development - AQA
Many of the Earth’s resources are finite. Chemists have a role in estimating the amount of reserves remaining and ensuring that the use of resources is sustainable.

Water - AQA
All humans rely on safe drinking water. Salt can be removed from sea water to make it safe to drink. Waste water must be treated before being released into the environment.

Ways of reducing the use of resources - AQA
Life-cycle assessments can evaluate the environmental impact of a product. Many products are recycled to lessen environmental impact. Modern metal extraction can reduce the impact on the environment.

Using materials - AQA
Metals have many properties but some are prone to corrosion. Alloying metals improve their properties. Ceramics, polymers and composites have desirable properties that allows them specific uses.

Fertilisers - AQA
Fertilisers contain elements which are essential for the healthy growth of crops. Fertilisers can be made in the laboratory and on a larger scale by the chemical industry.

Sample exam questions - using resources - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Practical skills
Planning an experiment
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link