Watch: How a circuit works
Everything you own that uses electricity will have an electric circuit. These circuits are made up of different electrical components.
Learn how an electric circuit works.
VOICEOVER: "The battery pushes electricity along the wires from the positive terminal, through the bulb, back to the negative terminal of the battery making a circuit. Electricity can travel easily though the metal wires in the circuit.
To turn out the light we need to break the circuit. We can do this by putting in a switch. It doesn't matter where in the circuit you put the switch - the effect is the same.
The bulb glows because electricity flows through the thin wire inside the bulb called a filament and makes it hot. When the bulb gets old, the wire will eventually break, breaking the circuit and therefore no electricity can flow. Time to change the bulb!"
The battery

A circuit always starts with a battery. A flow of electricity moves from the positive pole to the negative pole of the battery.
The flow is pushed by the battery, through the wires to the other components in the circuit. This makes a complete electrical circuit.

Switches, bulbs, buzzers and voltage
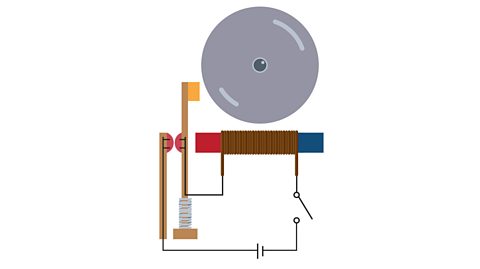
A switch breaks the circuit and the flow of electricity stops. The switch can be used anywhere in the circuit to stop the flow of electricity through a component.
Bulbs glow and buzzers sound when electricity passes through them.
Voltage (V) is the âpushâ which makes the electricity flow around a circuit. Circuits with lots of components need more voltage because they need more electrical energy pushed to them. The more batteries, a higher voltage means bulbs will be brighter and buzzers will be louder.
Activity 1: Tap the components
Activity 2: Components quiz
Activity 3: Draw the circuits

You may need a pen and paper for this activity.
- Draw a diagram of a circuit with three bulbs and three batteries.
- Cover two of the batteries. What would happen to the bulbs?
- Uncover the batteries and cover two bulbs. What would happen to the single bulb?

Where can should you place a switch in this circuit?
You can place a switch anywhere in the circuit and it will have the same effect.
Bitesize Primary games. gameBitesize Primary games
Play fun and educational primary games in science, maths, English, history, geography, art, computing and modern languages.

More on Electricity
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 6

- count2 of 6

- count3 of 6

- count4 of 6
