Area
Area is the amount of space taken up by a surface or 2-D shape. It is measured in squares with metric units mm², cm², m² and km².
Areas of rectangles, triangles, simple compound shapes and circles is covered in Geometry & measures - area
Calculate the areas of kites, parallelogram, rhombuses, trapeziums and compound shapes.
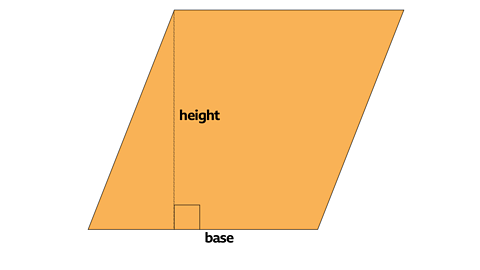
Calculating areas of Parallelograms
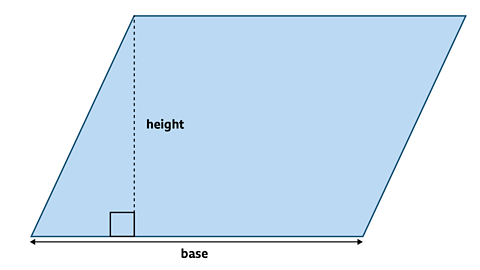
A parallelogram is a 2-D shape with 2 pairs of parallel sides.


When this triangle is moved from the left-hand side of the parallelogram to the right-hand side the area remains the same but shape is now a rectangle.
The area of a parallelogram is the same as the area of the rectangle.
Example
Calculate the area of this parallelogram.
Solution
Area of a parallelogram = base x perpendicular height
Area = 9 x 6 = 54 cm²
Calculating Areas of Kites
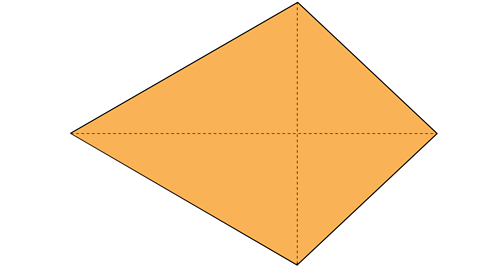
A kite is a 2-D shape with 2 pairs of equal sides. The diagonals cross at right angles.

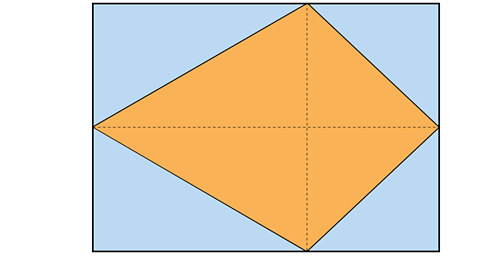
When a rectangle is drawn around the kite with the length and width equal to the diagonals of the kite it is clear to see that the rectangle has twice the area of the kite.
Therefore, the area of a kite can be found by multiplying the two diagonals and then dividing the answer by two.

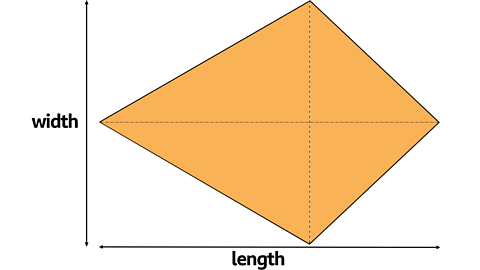
Area of Kite = length x width Ă· 2
Or multiply the diagonals and divide by 2

Example
Calculate the area of the kite.
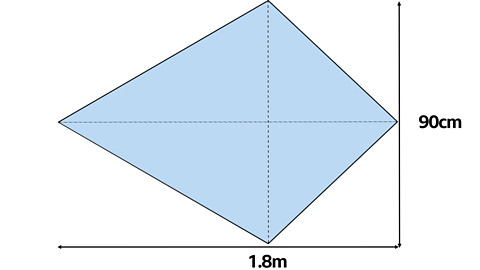
Area of Kite = length x width Ă· 2
Or multiply the diagonals and divide by 2
The diagonals are 90 cm and 1.8 m
Firstly change 90 cm into metres.
90 cm = 0.9 m
Area = 1.8 x 0.9 ÷ 2 = 0.81 m²
Calculating the area of a rhombus
A rhombus is both a parallelogram and a kite. The area can be calculated using either method.
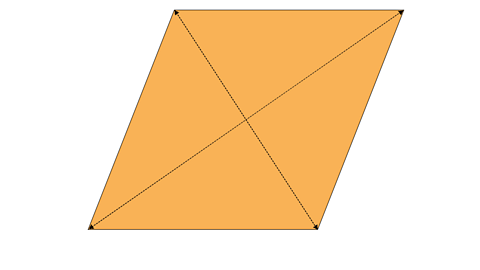
Example
Calculate the area of the rhombus.
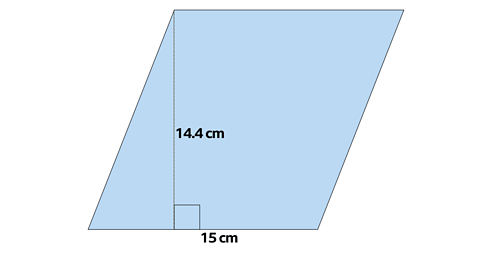
In this rhombus the base and the perpendicular height are known so the area is calculated using
Area of a parallelogram = base x perpendicular height
Area = 15 x 14.4 = 216 cm²

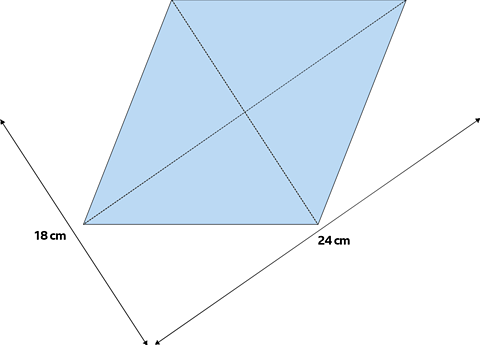
The same rhombus has the lengths of the diagonals known so the area is calculated by
multiply the diagonals and dividing by 2
Area = 24 x 18 ÷ 2 = 216 cm²
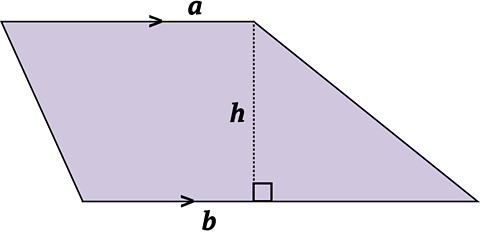
Calculating the Area of a Trapezium
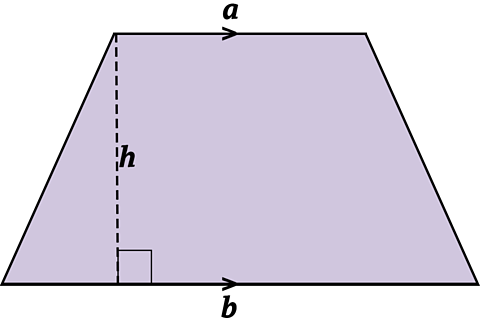
A trapezium is a 4 sided shape with one pair of parallel sides.
The area of a trapezium is calculated using the formula:
\(\mathbf {Area = \frac{1}{2}(a + b)h}\)
\(a\) and \(b\) are the parallel sides
and \(h\) is the perpendicular height.

Some trapezia/trapeziums look a little different. Take care to identify the parallel sides before using the formula.
Example
Calculate the area of this trapezium.
\(\mathbf {Area = \frac{1}{2}(a + b)h}\)
- \(a = 58mm\)
- \(b = 45mm\)
- \(h = 50mm\)
\(Area = \frac{1}{2}(58 + 45)50 = 2575 mm^2\)
Test yourself
More on M2: Geometry and measures
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 4