Key points
Carbohydrates are compounds that are found in living things. Their molecules are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy in a healthy diet. Starchy and sugary foods are high in carbohydrates.
Athletes eat different types of carbohydrate at different times in their training schedules.
Game - testing for sugar
Play an Atomic Labs experiment to find the sugar content of different foods.
You can also play the full game
Types of carbohydrates
The main types of carbohydrates are:
- Simple carbohydrates (also known as sugars)
The basic units of carbohydrates are simple sugar molecules, for example glucose, fructose and sucrose. They are provided by sweet foods like chocolate, milk and fruit.
- Complex carbohydrates (also known as starch)
These are formed of long chains of sugars joined together. They are found in foods like bread, rice, pasta and potatoes.
How does your body use carbohydrates?

Carbohydrates are an important source of energy. They fuel the processes in your body.
Carbohydrates are broken down by the body into glucose, which can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Once absorbed, glucose molecules travel in the blood to the body's cells where they are used for respiration. The glucose reacts with oxygen, releasing energy.
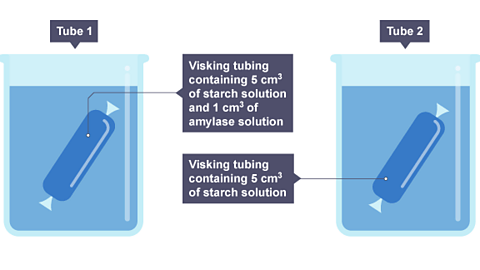
Starch and sugars are digested differently by the body:
Sugary foods and drinks can be quickly broken down to make glucose. This can be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream to provide a short-lasting energy boost.
Starch is a long, complex molecule which is harder to break down into glucose. This means that it releases energy more slowly. As such, it is known as a slow-release carbohydrate.

How much carbohydrate do you need?
The World Health Organisation recommends getting half your energy from carbohydrates. For a moderately active teenager, this is about 260 g daily.
Who needs to know about carbohydrates?

Athletes need different types of carbohydrate for different situations.
Before a short race, an athlete might eat a sweet banana for an âenergy boostâ.
Before a long training session, an athlete might eat plenty of starchy pasta for a steady supply of energy.

Quiz - Carbohydrates
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Nutrition, digestion and excretion
Find out more by working through a topic
- count12 of 15

- count13 of 15
- count14 of 15
- count15 of 15

