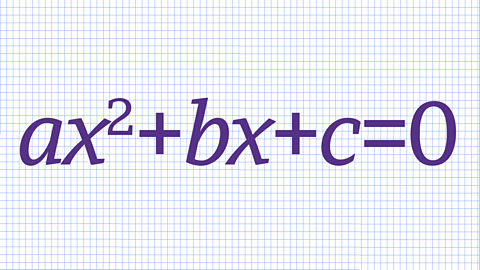Equation of a straight line
Before you start, it may be helpful to read the guides on coordinates and graphs from and .
Reminder
- The line \(y = mx +c\) has a gradient \(m\) and an intercept \(c\)
- Parallel lines have the same gradient
Gradients of perpendicular lines
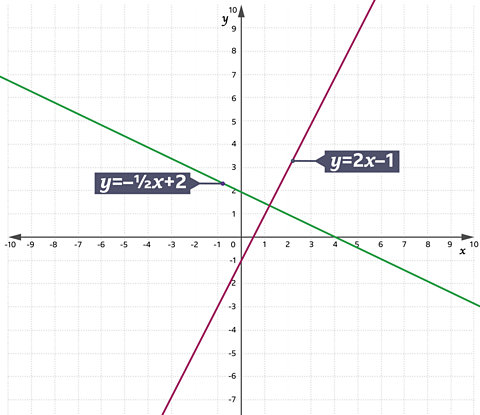
When two lines are perpendicular, the product of their gradients is 1.

Lines A and B are perpendicular.
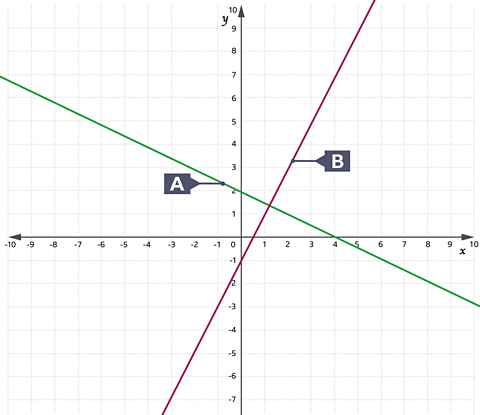
Line A \(m=â\frac{1}{2}\)
Line B \(m=2\)
°À(2°ÀłÙŸ±łŸ±đČőâ\ŽÚ°ùČ賊”ś1°š”ś2°š=â1°À)
Product of gradients \(=â1\)

Example
A line Lâ has the equation \(3y = 2x - 5\).What is the equation of the line Lâ which goes through (4, -4) and is at right angles to Lâ?
Solution:
Divide Lâ by 3 to get \(y = \frac{2}{3}x -\frac{5}{3}\)
\(m = \frac{2}{3}\)
For Lâ
\(m = - \frac{3}{2}\)
To find the gradient of a perpendicular line, turn the given gradient upside down and put a minus sign in front.
Let equation of Lâ be \(y = mx + c\)
\(y = - \frac{3}{2}x + c\)
Goes through (4, -4) substitute x = 4, y = -4
\(-4 = - \frac{3}{2}(4) + c\)
\(-4 = -6 + c\)
\(c = 2\)
Equation is \(y = - \frac{3}{2}x + 2\)
It is usual to eliminate fractions from the equation of a line by multiplying across by the denominator of the fraction.
\(2y = -3x + 4\)
or \(2y + 3x = 4\)
Alternative solution:
Use the formula \(y - y_1 = m (x - x_1)\) for Lâ
\(m = - \frac{3}{2}\)
\(y - (-4) = - \frac{3}{2}(x -4)\)
\(y + 4 = - \frac{3}{2}(x -4)\)
Multiply across by 2
\(2y + 8 = - 3(x -4)\)
\(2y + 8 = - 3x + 12\)
Equation of Lâ \(2y + 3x = 4\)
Question
Find the equation of the line which is perpendicular to \(y + 4x = 2\) and which passes through the point (10, 4).
Answer:
Use the formula \(y - y_1 = m (x - x_1)\)
\(m = \frac{1}{4}\)
\(y - 4 = \frac{1}{4}(x - 10)\)
Multiply across by 4
\(4y - 16 = x - 10\)
\(4y - x - 6 = 0\)
Example
Find the equation of the line which is the perpendicular bisector of the line joining (5,5) and (-5, -1).
Answer:
Mid point of the line (5,5) and (-5, -1) is (0, 2)
\(\matrix{~x & ~y \cr ~5 & ~5 \cr -5 & -1 \cr \hline ~0 & ~4}\)
Divide each by 2 to give mid point of (0, 2).
Let equation of the line which is the perpendicular bisector be \(y = mx + c\)
It goes through (0, 2).
Gradient of line joining (5,5) and (-5, -1) = \(\frac{\text{difference in y values}}{\text{difference in x values}} = \frac{5-(-1)}{5-(-5)} = \frac{6}{10}\)
Gradient of perpendicular line = \( - \frac{10}{6} \)
\(m = - \frac{10}{6} \)
It goes through (0, 2).
Substitute x = 0, y = 2 and \(m = - \frac{10}{6} \)
\(2=- \frac{10}{6}(0) + c\)
\(c = 2\)
Equation is \(y =- \frac{10}{6}x + 2\)
Multiply by 6
\(6y =-10x + 12\)
Question
The line AB is drawn on a grid as shown below.
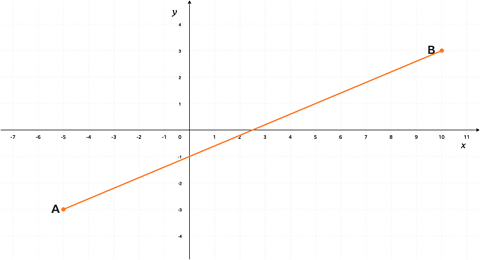
Show that the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB has the equation \(4y +10x = 25\)
Answer:
The co-ordinates of the points A and B are (-5, -3) and (10, 3).
Mid-point of AB is \(( \frac{-5+10}{2},\frac{3-3}{2})\)
\((\frac{5}{2},0)\)
Gradient of AB is \(\frac{-3-(-3)}{10-(-5)}~=~\frac{6}{15}~=~\frac{2}{5} \)
Gradient of perpendicular bisector \( = - \frac{5}{2}\)
Using \(y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)\)
Equation of perpendicular bisector \(y - 0 = \frac{5}{2}(x-\frac{5}{2})\)
Multiply across by 2 \( 2y = -5(x - \frac{5}{2} )\)
Rearrange \( 2y = -5x + \frac{25}{2}\)
Multiply across by 2 \( 4y = -10x + 25\)
\(\mathbf{4y + 10x = 25}\)
It can often be simpler using y = mx +c
\(y= - \frac{5}{2}x + c\)
\(0= - \frac{5}{2}(\frac{5}{2}) + c\)
\(c= \frac{25}{4}\)
\(c= \frac{25}{4}\)
Equation is \(y = - \frac{5}{2} x + \frac{25}{4}\) (multiply by 4)
\(\mathbf{4y + 10x = 25}\)
Test yourself
More on M4: Algebra
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 4