Watch: Introduction to geographical fieldwork
Play the video to watch Ayesha and James learn about human and physical features at Hadrianâs Wall.
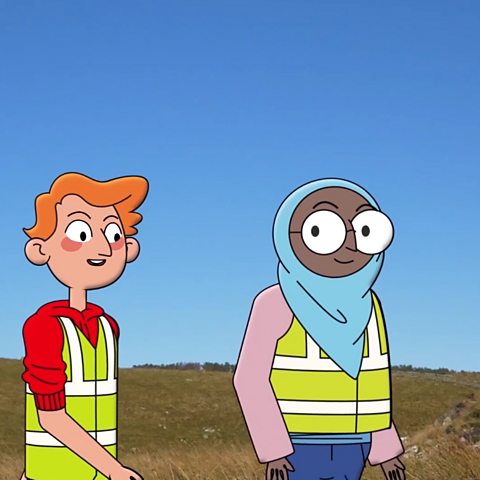
James: Hadrian's Wall is amazing! It was built by the Romans nearly two thousand years ago! We're so lucky to be doing our geography fieldwork here, to see how this place has changed!
Ayesha: It's great! I think the best thing is the view and the wildlife.
James: Yeah! We're really high up here. It must have taken them ages to build it this high.
Ayesha: Erm. It kind of helps that they built it on top of the hills though.
James: Oh⊠Yeah⊠I guess!
Ayesha: The wall is built on the edge of the rocks all the way along, which is why it's kind of wobbly.
Teacher: Well spotted!
Ayesha and James: Hello Miss!
Teacher: That wobble is a perfect example of where physical geography has influenced human geography. Did you know that physical features are anything that has formed naturally and that humans haven't made. Things like rivers, lakes, oceans and even volcanoes!
Ayesha: Ah⊠So the hills are physical features?
Teacher: That's right!
James: Human features are things that have been built, like houses, towns and cities. So that means the wall is a human feature.
Teacher: Well remembered!
Ayesha: I'm going to take a picture of it for our project.
James: Hey! That's great, but you haven't got as much of the wall in as they have in this guidebook.
Ayesha: I'm going to take a few from different angles. I can print them and put them together like a collage.
Teacher: Hmm. I can see you two are taking gathering your primary sources very seriouslyâŠ
James: Absolutely!
Ayesha: My pictures look a bit different from the ones in the guidebook.
Teacher: That's because the pictures you've taken are your primary sources. It's interesting to compare them with the ones in the guidebook, which is itself a good secondary source.Yes, some of these really are quite different.
Ayesha: Mainly because they don't have James's face in themâŠ
What do you need to think about?

Fieldwork is when you go outside the classroom and find things out for yourself.
When carrying out fieldwork, you will need to think like a geographer. What is the field work? Where and how will you carry it out? And why will you be doing it?
What?
- observe
- plan
- question
- research
Where?
- use maps and plans to explain where places are
How?
- collect and record data to explain what people, places and environments are like
- stay safe
Why?
- think about connections between human and physical features
- present your findings using maps, pictures, charts, diagrams and writing

What are human and physical features?
Fieldwork includes investigating both human and physical features.

Human features are things that have been built, such as:
- houses
- towns
- cities
- walls
- roads


Physical features are anything that has formed naturally and that humans havenât made, such as:
- rivers
- lakes
- oceans
- volcanoes
- mountains
What are sources?
Information can be found in both primary and secondary sources.
Fieldwork involves collecting primary sources of information.

Primary sources of information are things that were collected at the time, and include:
- photographs
- diaries
- videos

Secondary sources of information are usually based on primary sources, such as:
- magazines
- textbooks
- guidebooks
- newspapers

Take a look at some features and sources
Examples of human and physical features, and primary and secondary sources of information:

Image caption, Human and physical features
Hadrianâs Wall is a human feature, built on top of a hill - which is a physical feature.
Image caption, Edinburgh Castle
Edinburgh Castle was built on what is left of an extinct volcano. It was built as high as possible to help stop it being attacked.
Image caption, Primary source of information
When you take a photograph it is a primary source of information.
Image caption, Primary source of information
The data you collect is a primary source of information.
Image caption, Secondary sources of information
Video documentaries are secondary sources of information.
Image caption, Secondary sources of information
Information books and online searches are secondary sources of information.
1 of 6
Activities
Activity 1: Think like a geographer!

Draw a cartoon image of yourself as âgeographerâ and annotate it with your geography toolkit.
- What would be in your geographerâs kit bag?
- What skills would you be using?
- What kind of fieldwork questions would you ask?

Activity 2: Quiz â Geographical fieldwork
Bitesize Primary games. gameBitesize Primary games
Play fun and educational primary games in science, maths, English, history, geography, art, computing and modern languages.

More on Fieldwork
Find out more by working through a topic
- count9 of 12

- count10 of 12
- count11 of 12
