Properties of triangles
Properties of triangles
The angles in a triangle add up to \({180}^\circ\).
The properties of different kinds of triangles are listed below.
Equilateral triangle
- sides are of equal length
- all angles are equal (\({60}^\circ\))
Isosceles triangle
- two sides are of equal length
- two angles are equal (called the base angles)
Scalene triangle
- the three sides are all different lengths
- none of the angles are equal
Right-angled triangle
- contains a right angle
- can be either isosceles or scalene
Acute-angled triangle
- all three angles are acute
- can be equilateral, isosceles or scalene
Obtuse-angled triangle
- contains an obtuse angle
- can be either isosceles or scalene
Key point
Within all triangles, the longest side is opposite the largest angle, and the shortest side is opposite the smallest angle.
If two, or three, angles are the same size, then the sides opposite are of equal length.
Properties of quadrilaterals
The angles in a quadrilateral add up to \({360}^\circ\).
The properties of different kinds of quadrilaterals are listed below.
Square
a square is the only regular quadrilateral
all angles are equal \(({90}^\circ)\)
all sides are of equal length
opposite sides are parallel
the diagonals bisect each other at \({90}^\circ\)
the diagonals are equal in length
Rhombus
with a rhombus, all sides are of equal length
opposite sides are parallel
diagonally opposite angles are equal
the diagonals bisect each other at \({90}^\circ\)
Rectangle
with a rectangle, all angles are equal \(({90}^\circ)\)
opposite sides are of equal length
the diagonals are equal in length
opposite sides are parallel
the diagonals bisect each other
Parallelogram
with a parallelogram, diagonally opposite angles are equal
opposite sides are of equal length
opposite sides are parallel
the diagonals bisect each other
Trapezium
- with a trapezium, one pair of opposite sides is parallel
Kite
with a kite, two pairs of sides are of equal length
one pair of diagonally opposite angles is equal
only one diagonal is bisected by the other
the diagonals cross at \({90}^\circ\)
Key point
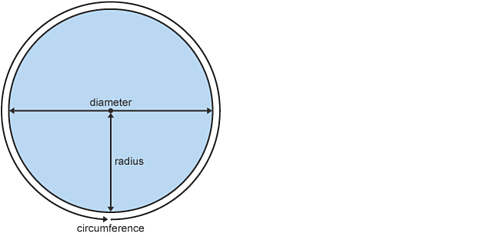
Other 2D shapes are considered in the article on polygons and circles.
Test section
Question 1
Which 2D shape is this?
Answer
This is a trapezium as it has only one pair of parallel sides.
Question 2
Which name best describes this triangle?
Answer
This triangle is both right-angled and isosceles.
Question 3
Which of these quadrilateral shapes does not have perpendicular diagonals (ie crossing each other at \({90}^\circ\))?
a) Kite
b) Square
c) Rectangle
Answer
Although the angles at the vertices of a rectangle are right angles, the diagonals do not cross at \({90}^\circ\)
Question 4
Which of these shapes does not have \({2}\) pairs of opposite sides of equal length?
a) Kite
b) Parallelogram
c) Rectangle
Answer
A kite has two pairs of sides of equal length, but that they are not opposite each other.
More on Shape, space and measures
Find out more by working through a topic
- count43 of 52
- count45 of 52

- count46 of 52