Further chemical reactions, rates and equilibrium, calculations and organic chemistry
Metals and reactivity series - (CCEA)
The reactivity series ranks metals by how readily they react. More reactive metals displace less reactive metals from their compounds and react with water.

Redox, rusting and iron - (CCEA)
Oxidation is loss of electrons, gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen. Reduction is gain of electrons, loss of oxygen or gain or hydrogen. Rusting is an example of oxidation.

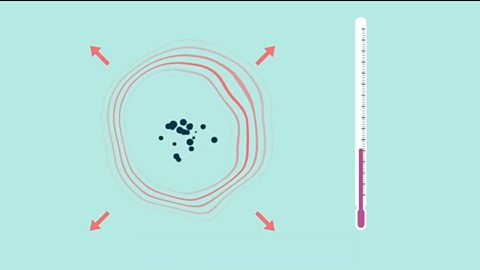
Rates of reaction - (CCEA)
The rate of reaction increases when reactant particles successfully collide more frequently. Temperature, reactant concentration, size of solid reactant particles (surface area) and catalysts can all affect the reaction rate.

Reversible reactions - (CCEA)
Some chemical reactions are reversible, and may reverse even as they react. This can create a state of dynamic equilibrium.

Organic chemistry - (CCEA)
An organic chemical contains the element carbon. There are four different homologous series of organic compounds discussed here: alkanes, alkenes, alcohols and carboxylic acids.

Quantitative chemistry - (CCEA)
We looked at calculating and using moles for solids using mass in unit 1.7. Here we are using moles of a solute dissolved in a solution and moles of a gas to carry out calculations.

Electrochemistry - (CCEA)
Electrolysis involves using electricity to break down electrolytes. The products of electrolysis can be predicted for a given electrolyte.

Energy changes in chemistry - (CCEA)
When a chemical reaction occurs, energy is transferred to, or from, the surroundings. An exothermic reaction releases heat to the surroundings and an endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
Gas chemistry - (CCEA)
The Earth atmosphere is a mixture of gaseous elements and compounds. We can prepare samples of common gases such as hydrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide in the laboratory and examine their properties and reactions.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link