Metabolism for survival
Metabolic pathways
Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions that take place inside living cells. Unicellular and multicellular organisms must control their metabolism in order to survive.

Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration refers to the breakdown of glucose and other respiratory substrates to make energy carrying molecules called ATP.

Metabolic rate
Metabolic rates can vary depending on physiological states. The circulatory system and respiratory system play a crucial role in ensuring efficient delivery of oxygen to cells around the body.
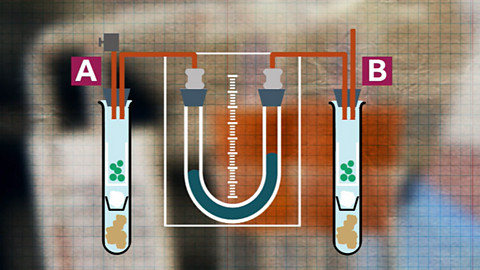
Metabolism in conformers and regulators
Conformers’ internal environment depends on the external environment. Regulators control their internal environment through their metabolism. Both must regulate their temperature to maintain optimum metabolic rate.

Metabolism and adverse conditions
Some animals can survive extreme conditions that are beyond the limits of their normal metabolic activity. Adaptations to achieve this include dormancy and migration.

Environmental control of metabolism
Micro-organisms include prokaryotes (archaea, bacteria) as well as some species of eukaryotes. They can be grown in laboratories and require specific conditions in order to grow.
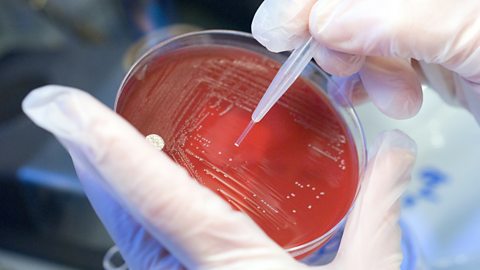
Genetic control of metabolism
The metabolism of a micro-organism can be controlled genetically and can involve mutagenesis and recombinant DNA technology.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link