Key concepts in chemistry
Equations and formulae - Edexcel
Chemists use symbols and formulae to represent elements, ions and compounds. Word equations and balanced chemical equations model the changes that happen in chemical reactions.

Hazards and risks - Edexcel
Hazard symbols warn about the dangers of a substance. Risk is the chance that a hazard will cause harm. Risk assessments describe how to reduce the risk of harm when carrying out an experiment.

Atomic structure - Edexcel
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. The numbers of particles in an atom can be calculated from its atomic number and mass number.

The periodic table - Edexcel
Mendeleev made an early periodic table. In the modern periodic table, elements are in order of atomic number in periods and groups. Electronic configurations model how electrons are arranged in atoms.

Ionic compounds - Edexcel
When a metal element reacts with a non-metal element an ionic compound is formed. They have a giant lattice structure with strong ionic bonds. A lot of energy is needed to overcome these bonds.

Simple molecular substances - Edexcel
A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonding results in the formation of molecules. Simple molecular substances have low melting and boiling points, and do not conduct electricity.
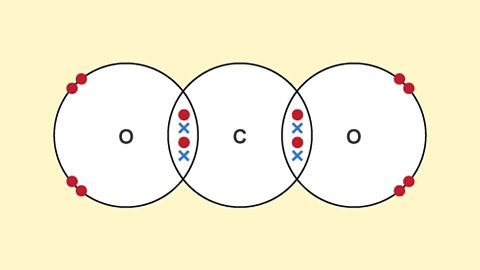
Giant covalent substances - Edexcel
Giant covalent substances contain atoms joined together by bonds. Diamond, graphite and graphene are forms of carbon and have different properties because they have different structures.

Metals and non-metals - Edexcel
Metals and non-metals have different properties. Properties of metals can be explained in terms of metallic structure and bonding. Different chemical models have different features and limitations.

Chemistry calculations - Edexcel
An empirical formula of a substance is found using the masses and relative atomic masses of the elements it contains. The law of conservation of mass applies to closed and non-enclosed systems.

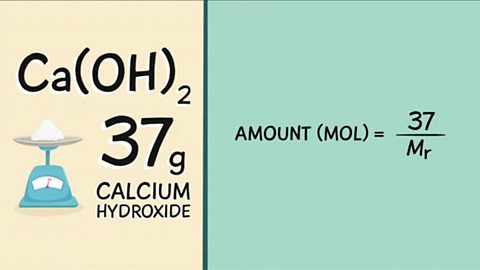
Mole calculations (higher) - Edexcel
The mole is the unit for the amount of substance. The number of particles in a substance can be found using the Avogadro constant. The mass of product depends upon the mass of limiting reactant.
Sample exam questions - key concepts in chemistry - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions. Arrangements for exam/non-exam assessments for students taking qualifications during the pandemic may be subject to change. Please check with your teacher.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link