Chemical changes and structures
Rates of reaction
The speed of a chemical reaction is affected by temperature, concentration, particle size and the presence of a catalyst. It can be calculated by measuring changes in reactants/products.

Atomic structure
Atoms are made from protons, neutrons and electrons. In this study guide, you can revise how the periodic table arranges elements according to their atomic size and other properties, atomic theory and atomic numbers, you'll also learn about isotopes and the properties of the main groups of elements.

Bonding and properties of materials
Only the noble gases exist as individual atoms not bonded to other atoms. In all other substances atoms are held together by chemical bonds, either sharing or gaining/losing electrons.

Chemical formulae
The chemical formula for a substance shows how many atoms of each element are present in a molecule, or the proportion of atoms of each element. The formula can be worked out using the valency.

Balanced equations
Chemical equations must be balanced so that the quantities of reactants and products match. For an equation to be balanced there must be an equal numbers of atoms on each side.

The mole and concentration of solutions
The gram formula mass of a substance is known as the mass of one mole. The mass, number of moles, concentration or volume of a substance can be calculated easily if you learn two formula triangles.

Acids and bases
The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. A pH less than 7 is acidic. Alkalis dissolve in water to give a pH greater than 7. A pH equal to 7 indicates a neutral solution.

- 13 videos
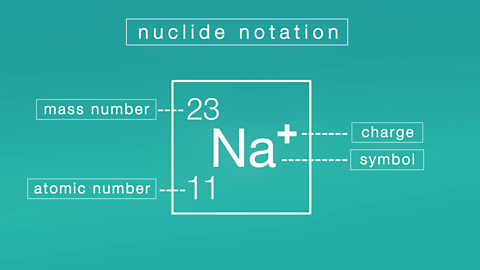
Nature's chemistry
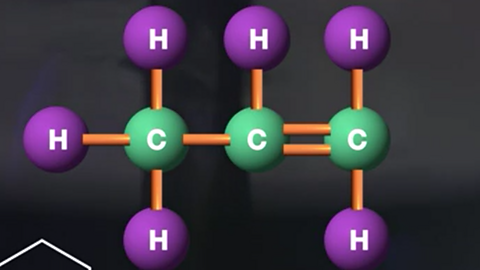
Homologous series
The alkanes, alkenes and cycloalkanes are examples of homologous series. A homologous series is a group of chemicals which have similar chemical properties and can be represented by a general formula.
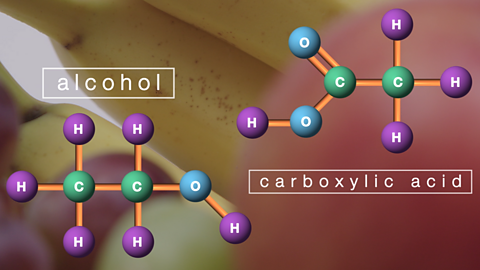
Everyday consumer products
An alcohol is a carbon compound which contains the hydroxyl group. Alcohols are used as fuels and solvents. Carboxylic acids are used in the preparation of soaps, medicines and preservatives.
Energy from fuels
When fuels burn they release heat energy and light energy to the surroundings in exothermic reactions known as combustion reactions. The energy released can be calculated using the equation Eh=cmâT.

- 8 videos

Chemistry in society
Metals
We use metals in everyday life, for example in jewellery or cars. They have many uses due to their properties which include strength, malleability, conduction of electricity and conduction of heat.

Plastics
Plastics are widely used as they have many useful properties. Most plastics and synthetic fibres are made from chemicals derived from crude oil and are made up of long chain molecules called polymers.

Fertilisers
There are two types of fertilisers: natural which is made from plant and animal waste, and artificial which is man-made. By using fertilisers, farmers are able to grow more crops on a field.

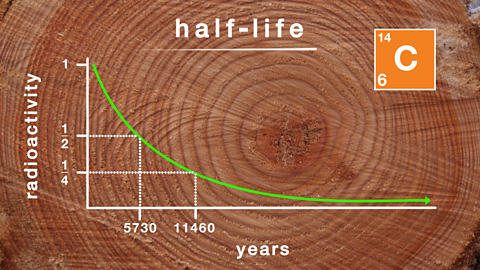
Nuclear chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is the study of the breakup of unstable nuclei, which results in the emission of radiation and energy. There are three types of radiation; alpha (α), beta (ÎČ) and gamma (Îł).

Chemical analysis
Chemists monitor our environment using a variety of quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques. The results from quantitative analysis are used in calculations that give essential information.

- 13 videos
Exam and assignment
Exam skills
The National 5 Chemistry exam is made up of a multiple choice paper and a written paper. Your exam will last 2 hours 30 minutes. The first paper is a multiple choice paper and the second paper is a written exam.

Researching Chemistry assignment
The Researching Chemistry assignment involves carrying out an experiment, comparing it to related research from literature or the internet and compiling this into a report.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link