Exam practice
GCSE Combined Science: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Combined Science past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.
GCSE Combined Science: exam-style questions
Free online CCEA Single Award foundation/higher science tests based on past papers to increase your understanding of biology, chemistry and physics GCSE exams.
GCSE Combined Science: quick-fire questions
Free interactive quiz questions based on CCEA Single Award GCSE combined science past papers to help you prepare for your biology, chemistry and physics GCSE exams.
Biology
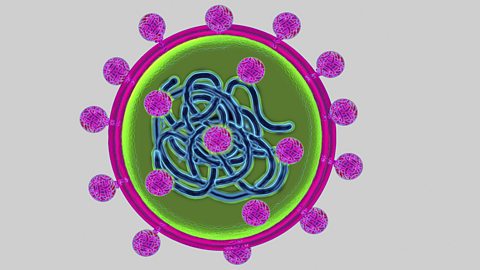
Microscopy and cells - (CCEA)
To examine cells and learn more about their structure, we need to be able to see them in very fine detail.

Nutrition and food tests (CCEA)
Food provides energy and nutrients. The different components of our diet have different sources and functions.

- Guide Number4 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides
- Guide Number4 Guides

- Guide Number3 Guides
- Guide Number3 Guides

- Guide Number4 Guides

Chemistry
Acids, bases and salts - (CCEA)
Many chemicals are acidic, neutral or alkaline. We can distinguish one from another using indicators. Acidity and alkalinity are measured on the pH scale.

Elements, compounds and mixtures - (CCEA)
Most elements are rarely found in their pure form. They are found chemically combined with other elements in compounds. Compounds are often found mixed with other compounds. Mixtures may be separated and analysed.

- Guide Number2 Guides

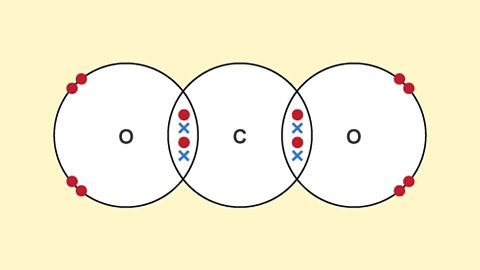
Bonding - (CCEA)
Atoms and ions bond with each other in two main ways â ionic bonds or covalent bonds. When these bonds are formed the atoms achieve a full outer shell of electrons and become stable.
Materials and their properties - (CCEA)
Materials can have many different physical properties which make them suitable for a range of purposes.

Symbols, formulae and equations - (CCEA)
Symbols, formulae and equations help chemists to explain chemical reactions in detail.

Qualitative analysis - (CCEA)
Qualitative analysis describes a range of chemical tests that can be carried out to identify a substance.

- Guide Number3 Guides

Rates of reaction - (CCEA)
The rate of reaction increases when reactant particles successfully collide more frequently. Temperature, reactant concentration, size of solid reactant particles (surface area) and catalysts can all affect the reaction rate.

Organic chemistry - (CCEA)
An organic chemical contains the element carbon. There are many different homologous series of organic compounds. Single Award Science focuses on alkanes and alkenes.

- Guide Number3 Guides

Practical skills - (CCEA)
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Physics
- Guide Number5 Guides

- Guide Number4 Guides

- Guide Number4 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number2 Guides
- Guide Number2 Guides

- Guide Number3 Guides

Practical skills
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription